Population of the USSR 1989. Population of the USSR by year: population censuses and demographic processes
The last census in the USSR was carried out on January 12, 1989. According to the last census of 1989, the population of the Soviet Union was 286.7 million people, including the urban population - 188.8 million people, or 66 percent.
The population of the RSFSR was 147.4 million people. Its distinctive feature was that for the first time, along with information about the population, information about housing conditions was collected. This made it possible to obtain information about the living conditions of various socio-demographic groups of the population in all regions of the country, about the development of housing cooperation, about the degree of provision of housing for people and its improvement.source.
As of 2010, there were 89,654,325 people left in Russia!


Here they are, the faces of the dictatorship of the World Financialcapital: RockefellerRichard, David Mayer Rothschild, Nathaniel Rothschild and others...



The Public Committee for Overcoming the Genocide of the Russian People informs you that according to the Central Analytical Center of the Russian Federation, Civil Registry Department, as of June 1, 2010, in the Russian Federation, according to documents, there are only 89,654,325 living people, and not 142,000,000, as officially stated in the population census.
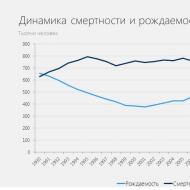
In 2009, 5,000,854 people died. In the period from January 1, 2010 to June 1, 2010, 4,678,856 people died. Every quarter the government records the reports of the Central Asian Center of the Russian Federation, but in reality the figures it publishes are completely different. Over the course of 10-15 years, a mortality rate of about 40,000,000 people is expected (data provided by Ekaterina Ulitina, an employee of the Central Asian Center of the Russian Federation, officially published in the newspaper “For Russian Business” 8 (160) for 2010, per. certificate 012225 MP of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 1993 .). http://www.zrd.spb.ru/zrd/2010/zrd_08-160.htm


The information has not been officially refuted. This circumstance allows us to consider it reliable. The fact of the criminal concealment of the monstrous KILLING of people indicates the deliberate creation by the occupation regime of the Russian Federation (in all its branches and subdivisions) of such living conditions that are designed for the complete physical destruction of the population of Russia.
Ref. 77-170211 from February 17, 2011 http://newsland.com/news/detail/id/650503/



According to official sources of information, the population of the USSR was constantly increasing, the birth rate was rising, and the death rate was falling. It’s like a demographic paradise in one country. But, in fact, everything was not so simple.
Population censuses in the USSR and initial demographic data
During Soviet times, seven all-Union censuses were conducted, covering the entire population of the state. The 1939 census was “superfluous”; it was carried out instead of the 1937 census, the results of which were considered incorrect, since only the actual population was taken into account (the number of people who are in a certain locality on the day of the census). On average, the population census of the republics of the Soviet Union was carried out every ten years.
According to the general census conducted back in 1897 in the then Russian Empire, the population was 129.2 million people. Only men, representatives of tax-paying classes, were taken into account, so the number of persons from non-tax-paying classes and females is unknown. Moreover, a certain number of people from the tax-paying classes hid in order to avoid the census, so the data is underestimated.

Population census of the Soviet Union 1926
In the USSR, the population size was first determined in 1926. Before this, there was no well-established system of state demographic statistics in Russia at all. Some information, of course, was collected and processed, but not everywhere, and only bit by bit. The 1926 census became one of the best in the USSR. All data was openly published, analyzed, forecasts were developed, and research was conducted.
The reported population of the USSR in 1926 was 147 million. The majority were rural residents (120.7 million). About 18% of citizens, or 26.3 million people, lived in cities. Illiteracy was more than 56% among people aged 9-49 years. There were less than one million unemployed. For comparison: in modern Russia with a population of 144 million people (of which 77 million are economically active), 4 million are officially unemployed, and almost 19.5 million are not officially employed.
The majority of the population of the USSR (according to years and statistics, demographic processes can be observed, some of which will be discussed in detail below) were Russians - almost 77.8 million people. Further: Ukrainians - 29.2 million, Belarusians - 47.4 million, Georgians - 18.2 million, Armenians - 15.7 million. There were also Turks, Uzbeks, Turkmens, Kazakhs, Kyrgyz, Tatars, Chuvashs, Bashkirs in the USSR, Yakuts, Tajiks, Ossetians and representatives of many other nationalities. In a word, it is truly a multinational state.

Dynamics of the population of the USSR by year
It can be said that the total population of the Union grew year by year. There was a positive trend, which, according to statistics, was overshadowed only by the Second World War. Thus, the population of the USSR in 1941 was 194 million people, and in 1950 - 179 million. But is everything really so rosy? In fact, demographic information (including the population of the USSR in 1941 and previous years) was kept secret, even to the point of falsification. As a result, in 1952, after the death of the leader, demographic statistics and demography were literally a scorched desert.
But more on that later. For now, let’s observe general demographic trends in the Land of Soviets. Here is how the population of the USSR changed over the years:
- 1926 - 147 million people.
- 1937 - the census was declared “sabotage”, the results were seized and classified, and the workers who carried out the census were arrested.
- 1939 - 170.6 million
- 1959 - 208.8 million.
- 1970 - 241.7 million
- 1979 - 262.4 million.
- 1989 - 286.7 million
This information is unlikely to make it possible to determine demographic processes, but there are also intermediate results, research, and accounting data. In any case, the population of the USSR by year is an interesting field for research.

Classification of demographic data since the early 30s
The classification of demographic information has been going on since the early thirties. Demographic institutes were liquidated, publications disappeared, and repression fell upon the demographers themselves. In those years, even the total population of the USSR was not known. 1926 was the last year in which statistics were collected more or less clearly. The results of 1937 did not suit the country's leadership, but the results of 1939, apparently, turned out to be more favorable. Only six years after Stalin’s death and 20 years after the 1926 census, a new census was carried out; according to these data, one can judge the results of Stalin’s rule.
The decline in the birth rate in the USSR under Stalin and the ban on abortion
At the beginning of the twentieth century, Russia had a really high birth rate, but by the mid-1920s it had decreased very significantly. The rate of decline in the birth rate accelerated even more after 1929. The maximum depth of the fall was reached in 1934. To normalize the numbers, Stalin banned abortion. The years following this were marked by some increase in the birth rate, but insignificant and short-lived. Then - war and a new fall.

According to official estimates, the population of the USSR grew over the years due to a fall in mortality and an increase in the birth rate. With the birth rate, it is already clear that everything was completely different. But as for mortality, by 1935 it had decreased by 44% compared to 1913. But many years had to pass for researchers to get to real data. In fact, the mortality rate in 1930 was not the declared 16 ppm, but about 21.
The main causes of demographic catastrophes
Modern researchers identify several demographic catastrophes that overtook the USSR. Of course, one of them was the Second World War, in which, according to Stalin, losses amounted to “about seven million.” Now it is believed that approximately 27 million died in battles and battles, which amounted to about 14% of the population. Other demographic catastrophes included political repression and famine.

Some events of demographic policy in the USSR
In 1956, abortion was allowed again, in 1969 a new Family Code was adopted, and in 1981 new child care benefits were established. In the country from 1985 to 1987. An anti-alcohol campaign was carried out, which somewhat contributed to the improvement of the population situation. But in the nineties, due to the deepest economic crisis, practically no actions were taken in the field of demography at all. The population of the USSR in 1991 was 290 million people.
All-Union Population Census of 1979
Just as during other population censuses, methodological and organizational issues were discussed at the All-Union Meeting of Statisticians in May 1974.
During the trial population census of 1976 in 9 districts and cities of the country, organizational and methodological programs for population census questions were tested.
The 1979 All-Union Population Census was conducted by survey method, the permanent and existing population was taken into account, and a sampling method was used (25% sample). An innovation of the population census was the use of a new form of census forms, which are also carriers of primary information.
Commuting migration was not taken into account in this census, but the counting of the non-working population of working age was retained.
The complete census program included the following questions: attitude towards the head of the family, notes on those temporarily absent and temporarily residing, age (year of birth), nationality (for foreigners - citizenship), native language and another language of the peoples of the USSR that is fluent, level of education, the type of educational institution in which one studies, the source of livelihood.
Sample census questions: place of work, occupation, social group, duration of continuous residence, number of live births.
The last question was new for all domestic population censuses and was included in accordance with the recommendations of international organizations for studying population reproduction.
The development of population census materials was carried out decentralized at cluster computing centers, and the calculation of results was carried out centrally in the central computing center of the Central Statistical Office of the USSR. A 5% sample survey was also carried out on the family composition of the population.
Preliminary census results were published in 1979; the first volume containing 31 tables of the complete census and 17 sample ones - in 1980-1983.
The All-Union Census (as of January 12, 1989) was the first post-war census that combined the demographic part with a census of the housing stock of the population.
The procedure for conducting the population census was based on the same principles as in other domestic population censuses: preliminary rounds, an eight-day census and sample control (25% sample). The permanent and existing population was enumerated; Complete and sample census forms were sources of machine information.
All preparations for the census were also quite traditional: a test census was carried out in December 1986 and in June-July 1987 in 10 regions and cities of the country. Census zoning, personnel selection and training, and mass explanatory work were carried out.
About 800 thousand census workers took part in the census. There were an average of 450 people per counting area in urban settlements, and 350 people in rural areas.
A comparison of the programs of post-war domestic population censuses shows that continuity has been preserved in the list of characteristics and, to some extent, even in the wording of questions. Evolutionary changes occurred very slowly, for example, the age question on the census form in 1959 was replaced by a question on age and date of birth (month, year) in 1970; about age and date of birth (year of birth, before January 17, January 17 or later) in 1979, and in 1989 transformed into a question about date of birth (day, month, year) and age.
In general, in this regard, of all the listed population censuses, only the 1970 population census program, when the sampling method was first used, was significantly expanded, and special tools made it possible to take into account employment and commuting in large cities.
The complete census program included the following questions: attitude towards the family member recorded first, gender, mark of temporary absence and temporary residence, date of birth and age, marital status, nationality, for foreigners - citizenship, native language, as well as another language of the peoples of the USSR , which is fluent, level of education, type of educational institution in which he studies, source of livelihood.
The sample census recorded the following characteristics: place of work, occupation, social group, duration of continuous residence in a given place, number of live births and living children.
The housing census consisted of the following questions: the period of construction of the house, the material of the external walls, the type of living space and its amenities, the number of living rooms, the size of the total and living space.
The main goal was to determine the living conditions of the family, and not to take a census of the housing stock, since the census covered only occupied residential premises. International statistical organizations offer extensive optional topics for population censuses in this area, where, in addition to the items taken into account mainly in the 1989 population census, questions were asked about rent, telephone coverage in the area, the presence of durable items in the household, cars, and own dachas. and garage, etc.
The development of population census data took three years. Preliminary census results were published in 1989. Later, the results of the population census were published in the Statistical Collection (1998) and in other publications.
this page is under construction
All-Union Population Census 1989
The last All-Union Population Census was carried out in January 1989 in accordance with Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated November 29, 1985 No. 174 “On the conduct of the All-Union Population Census in 1989.” The organization of preparation and conduct of the census is entrusted to the USSR State Committee on Statistics and its local bodies.
The moment of the 1989 census was 12 o'clock at night from 11 to 12 January. The census was carried out over 8 days, from January 12 to 19, 1989, through a survey at the place of actual residence of citizens. Information was recorded from the words of the respondents without requiring documents confirming the correctness of the answers. Two categories of the population were subject to registration - cash and permanent.
To ensure completeness of the population registration during the census, control measures were carried out - control forms and certificates of completion of the census were filled out, and random control walks were carried out. As a result of control activities, 0.4 million people were identified. unregistered persons. This number was included in the census results.
Preliminary results on the size and distribution of the population in individual regions of the country were published in April 1989, the final results were presented at the beginning of 1990.
The current population of the USSR, including foreign citizens living in the country, amounted to 286.7 million people, the RSFSR - 147.4 million people.
The 1989 All-Union Population Census in the Armenian SSR was carried out in an extremely difficult situation. The devastating earthquake and events in and around the Nagorno-Karabakh Autonomous Okrug led to intensive displacement of a large population both within the republic and outside its borders, which negatively affected the preparation and conduct of the census, as well as its results,
In the 9 regions most heavily affected by the earthquake (Amasia, Aragats, Artik, Akhuryan, Gugark, Gukasyan, Kalinin, Spitak, Stepanavan), as well as in the cities of Leninakan, Kirovakan, Dilijan, Spitak and Stepanavan, the census was carried out according to a reduced program and due to This means that for almost 600.0 thousand people no data was obtained on their marital status, family composition, sources of livelihood, living conditions, etc.
The State Statistics Committee of the Armenian SSR, based on automated processing of census forms, obtained final results on the size, age composition of the population, marital status and family size, level of education, nationality and languages, and sources of livelihood.
The current population of the Armenian SSR as of January 12, 1989 was 3287.7 thousand people. Compared to 1979, it increased by 256.9 thousand people, or 8.5 percent.
According to current records, the current population as of January 1, 1989 was 3,448.6 thousand people. The reason for the formation of such a large difference between the census data and the current population count lies in the extremely difficult situation in which the population census was carried out in the republic.
By the critical moment of the census, over 160 thousand people were evacuated from the disaster zone outside the republic and, naturally, they were not included in the current population.
In addition, more than half of the evacuees were not included in the permanent population of the republic, since second copies of census forms were not received for them. According to the census, the permanent population of the republic was 3304.8 thousand people and compared to 1979 it increased by 8.8 percent. The census results were also influenced by the rapid process of population migration associated with events in and around the NKAO.
Thus, the latest census data cannot serve as a sufficiently reliable basis for planning the prospects for the socio-economic development of the republic and therefore all results of subsequent analysis should be approached with a certain cost.
The population dynamics according to post-war census data were as follows.
Relatively high average annual population growth was observed in the 60s (66 thousand), due to higher birth rates and higher natural population growth, and since the beginning of the 70s, the average annual growth rate has decreased from 3.1 percent to 2.2 percent . In the 80s it decreased even more and amounted to 0.8 percent. or an average of 25.7 thousand people. in a year.
The urban population grew over ten years by 237 thousand people, or 11.9 percent. The share of city residents in the total population of the republic increased from 65.7 percent. in 1979 to 67.8 percent. in 1989.
Among the union republics, the most urbanized are the RSFSR (74 percent), the Estonian SSR (72 percent),
Latvian SSR (71 percent). At the same time, in the republics of Central Asia and the Moldavian SSR, less than half (33-47 percent) of the total population of these republics lives in urban settlements. The number of rural residents in the republic increased in the 80s by only 19.9 thousand people, or 1.9 percent; The main reason for the relatively low growth is the migration outflow of the rural population to cities.
The most important socio-demographic and economic characteristic of the population is its age-sex structure.
The age distribution of the republic's population is characterized by the following:

The current age structure reflects past trends in vital processes, especially fertility. They were greatly influenced by the Second World War, which not only claimed millions of lives, but also led to a decrease in the number of births both during the war and in the years when women born during the war, or the generation of their daughters, entered active childbearing age. This is largely responsible for the differences in the rate of population growth (or decline) for individual age groups between 1979 and 1989.
The consequences of the earthquake also had a certain impact. The number of deaths and evacuations outside the republic, for which no information was received, was disproportionate for all age groups.
Of particular interest from the point of view of the formation of labor resources is the size of the working-age population (men 16-59 years old, women 16-54 years old).

Over the past 10 years, the growth of the working-age population amounted to 118.4 thousand people, or 6.8 percent. In the country as a whole, their increase amounted to 7.0 million people. (4.6 percent), including almost 5 million (about 70 percent) in the republics of Central Asia and Kazakhstan.
In the 1980s, the process of population aging continued. The number of people over working age over the past period increased by almost 37.0 percent. or more than 4 times faster than the total population of the republic. As a result, the share of this age group increased from 9.3 to 11.7 percent over this period. However, the problem of population aging in our republic is not yet as acute as in some other regions of the country. In the country as a whole, this age group accounts for 17 percent. of the entire population, including in the RSFSR, Ukraine, Belarus and the Baltic states, 19-21 percent, and in the Central Asian republics - 8-10 percent.
Of the total population of the republic, men make up 1619.3 thousand (49 percent), and women - 1685.5 thousand (51 percent). There has been some improvement in the gender structure of the population. If in 1979 there were 948 men for every thousand women, then in 1989 there were 961. The excess number of women begins on average at the age of 20 and is caused by the higher mortality of men, although in rural areas this process begins much later, from 45 years of age.
The marriage structure of the population of the Armenian SSR in comparison with most union republics and the country as a whole is relatively satisfactory.

Over the past 10 years, the proportion of married people in Armenia has increased: men - from 65.4 percent. up to 70.4 percent; women - from 59.9 percent. up to 66.6 percent. At the same time, the proportion of divorced people increased: men - from 0.9 percent. to 1.0 percent, women - from 3.2 percent. up to 3.6 percent
For the country as a whole, this figure is 4.7 and 7.5 percent, respectively.
The highest proportion of divorced and separated persons is observed in Estonia and Latvia (about 7.0 percent among men and 10-11 percent among women), and the lowest in the republics of Transcaucasia and Central Asia (except Kyrgyzstan) - about 1-2 percent among men and 3-4 percent. among women.
The number of families according to the census was 558.5 thousand, which is 50.8 thousand families (8.4 percent) less than in 1979. The decrease in the number of families is explained by the fact that this did not include families living in earthquake areas. where the census was carried out according to an abbreviated program and information on the number and composition of the family was not collected, as well as some of the evacuated families for which information was not received.

There have been some shifts in the structure of families in terms of the number of members. Thus, the proportion of families of four increased and the proportion of families consisting of 6 or more people decreased. The latter is explained mainly by the massive outflow from the republic, mainly from rural areas, of people of Azerbaijani nationality, who, as a rule, have large families.
The average family size in the republic as a whole has not changed and is the same as ten years ago, 4.7 people, in urban areas 4.6 instead of 4.5 in 1979, in rural areas 4.9 instead of 5.2 people. The decrease in the average size of families in rural areas is explained by a decrease in the number of families of 6 or more people. This indicator was influenced both by the unsatisfactory state of affairs in housing construction in the republic and by the fact that information about this indicator was not received from part of the population of the republic (earthquake zone).

*) Without the population that completed the census according to the abbreviated program.
Today 96.3 percent live in families. population of the republic. In addition, 2.3 percent. family members live separately from the family, but are connected with it by a common budget. In the country as a whole, these figures are 89 and 5 percent, respectively. 1.4 percent have no family or have lost contact with it (singles). The share of family members living separately from the family and single people is also low in the republics of Central Asia, Georgia and Azerbaijan, where it is 4-6 percent, and is more significant in the RSFSR, Ukraine, Belarus, and the Baltic states (11-15 percent). .). This is partly due to differences in the number of elderly people living alone and a greater concentration of students in higher and secondary specialized educational institutions in the European part of the country.

For 1979 - 1988 The level of education of the population has noticeably increased. The number of people with higher and secondary (complete and incomplete) education increased over 10 years from 1708.2 to 2074.7 thousand people, or by 21.5 percent. Now more than 90 percent. of the republic's population aged 15 years and older have this level of education, versus 81.4 percent. in 1979. During the implementation of the Law on Universal Compulsory Secondary Education for Youth, the number of people with higher and complete secondary education grew at a relatively high rate. According to the current census, 71.5 percent. of the population aged 15 years and older have this level of education; in 1979 it was 56 percent. At the same time, the share of persons with incomplete secondary and primary education decreased from 36.9 percent. in 1979 to 25 percent. in 1989
The population employed in the national economy has a higher level of education than the general population. Among the employed, 95.4 percent have higher and secondary (complete and incomplete) education. versus 86.8 percent. in 1979
It is natural that over the same period the number of people employed in the national economy with primary education decreased by more than 2.5 times and now amounts to only 3.7 percent.
There was an equalization of the level of education of the urban and rural population. If in 1979 among city residents aged 15 years and older there were 87.1 percent. persons with higher and secondary (complete and incomplete) education, and among rural residents 70.0 percent, then in 1989, respectively, 93.5 percent. and 83.1 percent, i.e. the gap decreased by almost 7 points.
During the 1989 census, information was obtained on the population of all nationalities living in the Armenian SSR. Nationality, as in previous censuses, was indicated by respondents based on their self-awareness. The nationality of the children was determined by the parents.
For 1979-1988 the number of Armenians increased, and the share of other relatively numerous nationalities decreased or remained at the same level.

According to the latest census, the number of Azerbaijanis in the republic was 84.9 thousand people. It should be noted here that the number of people of Azerbaijani nationality living in the republic at the date of the census was 7.9 thousand people. The reason for the discrepancy of 77.0 thousand people is that the number of immigrants from Armenia who passed the census in the Azerbaijan SSR as a temporary resident population was included by the State Statistics Committee of the USSR in the permanent population of our republic.
During the period from 1979 to 1988, the number of Armenians living in the country increased by 472 thousand people, or 11.4 percent. This increase occurred in almost all union republics, with the exception of the two republics of Transcaucasia. There is a migration of the Armenian population here, mainly to Armenia; at a slower pace from Georgia and massive migrations from Azerbaijan.
*) According to the 1979 population census, the Yezidis were not separately identified and were included in the number of Kurds.

During the census, along with nationality, the native language and the second language of the peoples of the USSR, which the respondents speak fluently, were taken into account.

The data obtained indicate that 99.1 percent. Of the population of the republic, 0.9 percent consider the language of their nationality to be their native language. - the language of other peoples (in 1979, 98.8 percent and 1.2 percent, respectively).
According to the source of livelihood, the population of the republic was distributed as follows:

For 1979/1988 According to the census data, there is a decrease in the number of workers in the national economy and a sharp increase in the number of people who have other sources of livelihood and did not indicate the source, which is associated with the consequences of the earthquake, since information about the sources of livelihood, as well as costs, was not received regarding the population of the earthquake zone methodology for conducting a census in extreme conditions, when a significant part of the population was deprived of the opportunity to work on the census date.
The government of the republic is working to conduct a repeat population census after the situation in the republic has stabilized. Only the data of the new census can serve as a reliable basis for the development of long-term plans for the socio-economic development of the republic.
GOSKOMSTAT OF THE ARMENIAN SSR.