What is an insured event under compulsory motor insurance? Insured event under compulsory motor insurance
Civil liability insurance for car owners has been in effect in Russia since 2003. Until 2009, according to established rules, in order to receive compensation for damage received in insurance cases, victims had to contact the insurers of the person responsible for the accident. And here, according to legislators, there should not have been any problems with compensation for the damage caused to the victims.
However, in practice everything turned out to be not so rosy. Due to the large number of incomprehensible organizations involved in compulsory motor liability insurance and their dishonest attitude towards fulfilling their obligations to pay compensation in insured events, parties injured in road accidents often encountered problems in obtaining the required compensation.
At the same time, they could not in any way influence the successful resolution of the issue, and their insurance companies legally remained aloof from the problem of their clients. To resolve such situations, legislators in 2009 introduced an alternative direct compensation system (DRP) in addition to existing rules. This meant that in the event of an accident, the injured party could choose the method of receiving compensation from two possible options:
- the traditional method of contacting the insurer of the person responsible for the accident;
- An alternative method is to receive a direct payment from your insurance company.
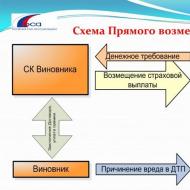
However, the introduction of PPV led to an increase in fraud and abuse among insurance companies, which was the reason for another revision of the rules for providing compensation for damage caused in road accidents. As a result, since 2014, a non-alternative PPV has been in force, which is a special procedure for compensating the costs of restoring a damaged car, received from the insurance company of the victim himself.
This system of direct loss settlement establishes direct instructions both for insurers who are obliged to finance repair work and in which insured events, and for policyholders in which insurance organization in which cases they should apply for compensation for damage. In the non-alternative PES system, the victim no longer has the opportunity to choose which insurance company to receive compensation from. For most insurance claims, the injured party's insurance company is the financing party.
Conditions of non-alternative PES
To receive compensation for damage under uncontested direct compensation from your insurance company, it is necessary that the insured event meets the following conditions:
- The consequences of a traffic accident should be exclusively damaged cars. If damage is caused to the health of people or structures, the insurance company of the guilty party will compensate for the damage.
- If before 09/25/17 one of the conditions was the mandatory participation of only 2 cars in an accident, now the number of injured cars involved in the incident is not limited. Do not confuse the PPV with self-registration of an accident without calling the traffic police, where the requirement for the presence of only two colliding cars remains unchanged.
- All participants in an accident interested in receiving compensation must have a valid MTPL agreement. In this case, the date of purchase of the policy does not play a role.
- The culprit of the incident and the victims must be clearly identified by the traffic police inspector. There should be no recognition of mutual guilt or challenge of the inspector’s decision by at least one of the participants in the accident.
- Insurance companies representing parties involved in accidents on both sides have signed PES Agreements and have valid government licenses.
Fulfillment of all the above conditions is mandatory; if the situation does not meet at least one of them, then an application for insurance compensation should be submitted to the insurer of the person responsible for the incident. At the same time, there is one more innovation - the victim has the right to apply to his insurance company to receive compensation, regardless of the entry in the policy as to who he is listed there as an insured or an owner. Previously, the discrepancy between the surnames of the owner and the insured served as a reason for the insurance company to refuse to pay compensation.
Cases where direct reimbursement is not made
Such cases include situations when:
- an application for compensation has already been submitted to the insurer of the guilty party;
- the victims incorrectly filled out their notification about the accident during the process of independently registering the incident using a simplified form without calling the traffic police representatives;
- there are disputes regarding the circumstances of the road accident among the participants in the accident;
- the victim seeks compensation for material profits lost as a result of the incident or only for moral damage received;
- The accident occurred during training driving, sports competitions or special tests;
- as a result of the incident, damage was caused to works of art, antique values, religious objects, and securities;
- the established cause of the accident is disputed by the culprit in court;
- the insurance company was not notified of the incident in a timely manner;
- the license of the insurance company of the person responsible for the accident is invalid or revoked;
- the insurance policy of the guilty party is expired (in this case, compensation for damage will have to be sought through the courts);
- The at-fault party's insurance company is not a member of the PES Agreement.
Receiving a refusal to pay compensation from your insurer should not be perceived as a complete refusal to pay insurance; it is only a redirection of the claim to the insurance organization of the guilty party or to the Union of Auto Insurers. However, it entails a longer period of proceedings and payment of insurance compensation.
Direct compensation procedure

The procedure for concluding an agreement on a PES occurs in several stages:
- Preparation of primary documents at the scene of the incident. This stage requires great care in drawing up the European Protocol or monitoring the correctness of the protocol by the traffic police inspector. The positive decision of the policyholder on the assignment of compensation payment and its amount largely depends on this.
- Preparation and submission of the required package of documents to the insurance company within five working days (see Federal Law No. 40, Article 11.1, paragraph 2, previously 15 days were provided for this).
- Study and analysis of information in the insurance company, making a decision on whether the incident is an insured event, paid on the principle of direct compensation.
- Inspection of the condition of the vehicle after an accident by representatives of the insurance company, assessment of the extent of damage and the amount of material damage caused. Often, insurance company experts underestimate the amount of damage received in order to reduce the amount of compensation, so it makes sense for the injured party to resort to the services of an independent expert in accordance with Article 12.1 of Federal Law No. 40.
- Payment of compensation is made no later than 30 days after filing the application. Compensation may be provided in the form of vehicle repairs. If a PES is refused, the company provides a reasoned official decision in writing.
- After compensation for damage to the injured party, its insurance company independently prepares documents for mutual settlements with the insurance organization of the person responsible for the accident, which compensates for their financial expenses.
List of documents required to obtain a PPV
To obtain a direct settlement from your insurance company, the injured party involved in the accident must submit the following documents:
- Application for direct compensation for losses under compulsory motor liability insurance. It is filled out on the insurance company’s form, received at the office or downloaded from its official website. The PES application is addressed directly to the organization itself, and not to its representative, otherwise a refusal may follow.
- A notification of a traffic accident, filled out by both participants in the accident, if it was completed by them independently according to the European Protocol without calling the police.
- A certificate of an accident in form 748, obtained from the traffic police inspector who prepared the accident report upon calling its participants.
- Copies of primary documents drawn up at the scene of the incident by the traffic police inspector (definition, resolution, protocol).
- A photocopy of the document indicating ownership of the vehicle that was damaged in an accident.
- Checks and receipts confirming the financial expenses incurred by the victim related to the consequences of the accident (payment for the services of a tow truck, an independent expert, etc.).
- A power of attorney in the name of your guarantor to receive allocated financial resources if necessary.

In addition to the above list of documents, the following papers may be required:
- photocopy of the insurance policy;
- details of the applicant’s bank for non-cash transfer of monetary compensation;
- photocopy of driver's license;
- photocopy of the applicant's personal passport;
- agreement on the amount of damage.
The last document is proposed for joint execution by a representative of the insurance company and is formal evidence of the insurance company fulfilling all its obligations to the injured party in this insured event. It specifies the timing, amount and procedure for payment of the established insurance amount. By signing this agreement, the applicant actually agrees with the established amount of compensation and is deprived of the opportunity to subsequently demand additional amounts for some previously unaccounted for reasons.
I got into an accident... What should I do? This is the first question that arises in the mind of an accident participant. Most people who are involved in such an incident are simply lost and do not know what to do and what documents to fill out. This material will help you gain the necessary knowledge and receive significant insurance payments in case of an accident.
What is OSAGO?
Some car owners still perceive taking out a policy as just another extortion; they confuse it with CASCO, believing that they are insuring their car. What is OSAGO? Auto liability insurance protects the property interests of its owner in the event of an accident.
If you are the culprit of an accident, the insurance company with which the contract is concluded will compensate for the damage you caused. If you are the injured party, then you need to contact the insurance company of the culprit. You can do this either independently or with the help of a representative of your insurer. It is very important to follow the procedure for compulsory motor liability insurance in case of an accident.
Payout limits
There is a maximum limit on the amount of insurance payout. For policies received before September 30, 2014, the following restrictions apply:

Due to changes in legislation, payment limits under contracts concluded from October 1, 2014 have been increased. Now each victim can count on payment of 400,000 rubles for damage caused to property, and 500,000 rubles for damage caused to life and health. The number of victims does not matter. The leader in the number of payments is Rosgosstrakh OSAGO. This insurer reviews the accident as quickly as possible and pays promptly.
First actions in case of an accident
If you are involved in an accident, there is no need to panic. It is necessary to soberly assess the situation and act strictly according to the instructions. The procedure for compulsory motor liability insurance in case of an accident can be read in the Road Traffic Rules (clause 2.5).

Photos from the accident scene should be as detailed as possible.
- Overall plan. Damaged vehicles and the roadway must be visible. From such a photo it is easy to determine what kind of place it is - a parking lot, the courtyard of a residential building, or a busy street.
- Take photographs of the condition of the road surface, brake marks, scattered parts and glass shards.
- Document the condition of vehicles using general photos of the front, rear, and sides. The numbers must be clearly visible.
- Take close-up photos of any damage.
Registration of road accidents under compulsory motor liability insurance
Motorists who find themselves in an unpleasant situation have 3 possible actions:
- call the traffic police and wait for them at the scene of the accident;
- report the incident by phone and, with the consent of the employees, fill out the documents yourself, and only after that go to the department;
- draw up a European protocol.
In the event of a collision of three or more vehicles, there are disputes about guilt in the incident, the nature of the damage, the refusal of one of the drivers to sign an accident notice, or if a preliminary assessment of damage exceeds 50,000 rubles, it is necessary to call a traffic police officer.
The paperwork regarding an accident can be completed at a stationary traffic police post within 24 hours if any reasons prevent the preparation of papers at the scene of the accident.
Registration of a European protocol is possible if several conditions are simultaneously met:
- Only 2 cars were involved in the accident; damage was caused only to vehicles (that is, no people were injured).
- Both drivers have valid MTPL agreements.
- The circumstances of the accident and the nature of the damage do not cause disagreement among drivers.
Thus, the procedure for compulsory motor liability insurance in case of an accident depends on the severity of the accident and the agreement of the participants in determining who is at fault.
In the presence of police officers
Depending on the nature of the accident, traffic police officers fill out a different set of documents.
If the accident resulted in personal injury:

If the accident results in damage only to property:
- a map of the scene of the incident is drawn up;
- explanations are collected from those involved in the accident;
- participants and victims are issued certificates of road accidents;
If administrative responsibility is not established, then a refusal to initiate a case is issued; if responsibility is established, a protocol on administrative violation is drawn up.
Preparation of the protocol
After the traffic police officer has drawn up a protocol and diagram of the incident, drivers must carefully read them and sign them, and if necessary, make their comments. What should you pay attention to when reading the protocol and diagram?
- The correctness of filling in your data, the nature of the violation, information about participants and witnesses.
- Check the completeness of the list of all damage to vehicles.
- There should be no missing lines in the protocol; do not sign a blank or incomplete document.
- The accident diagram must fully reflect the real state of things, road markings, signs, traffic lights and everything that matters in this case.
Various factors can influence the decision about guilt in an incident, which should be reflected in the documents. It can be:

If there are victims in an accident, and the inspector does not offer to undergo an alcohol test, you should do it yourself.
Europrotocol
The accident notification form is filled out by all participants in the accident, the circumstances of the incident and the nature of the damage are certified by their signatures. The amount of insurance payment under the European protocol cannot exceed 50,000 rubles. The victim cannot demand compensation from the insurer for damages exceeding this amount, but can make such demands against the perpetrator in court.
OSAGO insurance implies that the insurance company has the right to order an independent examination of the damaged vehicles if it finds contradictions in the description of the circumstances of the harm and the characteristics of the damage received in the accident notice.
In this case, vehicles cannot be repaired until a decision on payment is made.
Notification of an accident
To eliminate disputes and confirm agreement about the circumstances of the accident, the front side of the notification of a road accident is filled out by drivers together. If there are more than two participants, then the notice is filled out by the drivers of the nearest vehicles. If joint filling is impossible for any reason, they must be indicated in the document. Filling out the document by third parties (for example, due to the health condition of one of the drivers) is not allowed.
 In the absence of disagreements, two drivers may fill out one notice together. The insurance company must be notified of this. If there is a disagreement, each driver fills out a separate form.
In the absence of disagreements, two drivers may fill out one notice together. The insurance company must be notified of this. If there is a disagreement, each driver fills out a separate form.
The notice must indicate the presence of victims, and, if possible, information about them.
The front side of the document indicates the date, time, place of the accident, information about its participants, insurers, a list of visible damage and other information. The reverse side provides additional information.
The insurance payment may depend on the correct completion of this document, so it must be carefully checked. Pay attention to whether the other driver filled out his data correctly, whether he indicated the insurance policy number in full, and whether he put crosses everywhere.
List any visible damage to the vehicles. If you do not do this, it will be impossible to receive a payment for missed elements.
Submission of documents to the insurance organization
Within 15 working days, the injured party must provide the culprit’s insurer with all the necessary documents.
Documents in case of an accident (MTPL):
- application for insurance payment;
- completed accident report;
- protocol, resolution on refusal in a case of an administrative incident, resolution-receipt;
- certificate of accident;
- passport and vehicle registration certificate;
- driver's license;
- a copy of the power of attorney to drive the vehicle;
- vehicle assessment report (if done independently);
- payment documents on evacuation from the scene of an accident and storage of the vehicle (if available);
- bank account details.

Compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance in case of an accident
The insurer is obliged to make payment within 20 calendar days (except for holidays) from the date of filing the application. If the decision is delayed, the company is obliged to pay a penalty. If the victim is not satisfied with the amount of payment, he has the right to file a pre-trial claim, which is considered no longer than 10 days, and go to court. The payment will be maximum if you follow the procedure for compulsory motor liability insurance in case of an accident.
If an insured event occurs on a loan, but the insurance company does not pay, you can always appeal this decision in court.
Almost all loans today are accompanied by an offer from the bank to enter into an insurance agreement. The insurer is usually a partner company or a company that is part of a single holding structure along with the bank. Recently, classic insurance has begun to be replaced by financial protection programs, although, if you don’t go into legal details, these products do not have any special differences. In the consumer lending system, insurance is voluntary, and even if the bank managed to impose insurance, it can be refused. For mortgages and car loans, insurance is required, but this only applies to collateral.
In general, credit insurance is generally accepted practice, either on a voluntary or mandatory basis. And if the borrower takes out insurance, then, of course, he expects that if the insured event specified in the conditions occurs, he or the bank will be able to receive monetary compensation. But those who have already encountered issues with insurance payments note that even the most extended insurance does not provide a 100% guarantee of receiving money.
There is nothing special in the credit insurance system in terms of refusal to pay insurance that would not be encountered in other legal relations. The same reasons, the same arguments on the part of insurance companies. Only the consequences are somewhat different: you not only do not get what you expected and paid for, but you also remain in debt, and insurance thereby turns into a useless tool.
Unfortunately, the occurrence of an insured event in itself is not the only condition for payment of compensation. You also need to follow the procedure for contacting the insurance company and a number of other formalities. But you may encounter another situation in which the insurer will try in every possible way either to avoid fulfilling its obligations or to reduce the amount of payment to a minimum. Knowing your rights and skillfully using available tools to protect them is the main condition for effectively combating unscrupulous insurance companies.
How to interact with the insurance company in the event of an insured event
Whatever insured event occurs, first of all you need to make sure that it is indicated in the terms of the insurance contract. It just so happens that many borrowers do not read the agreement carefully when signing: at best, they will glance at it, and at worst, they will take the manager’s word for it. As a result, it may turn out that the event that happened to you is not specified in the contract at all. Or the wording is so vague that what happened can be viewed in the context of the terms of the contract in different ways. Unfortunately, if the case is not listed as insurable, you will not be able to claim compensation. If everything looks controversial and incomprehensible, be sure to contact a lawyer specializing in credit insurance. If there is an ambiguous interpretation, you are unlikely to figure out on your own who is right and who is wrong - you or the insurance company. In such a situation, judicial practice will also be of great importance, and here a specialist, in any case, is more competent than a legally unskilled person.
So, you have determined that the event is an insured event. How to proceed next:
- We carefully study the contract (policy), the memo of the insured person regarding the procedure (procedure) for contacting the insurance company (or bank) in connection with the occurrence of an insured event. The main task is to find out how, where and within what time frame it is necessary to submit the initial notification.
- We are preparing a notification. Usually, a fairly short period of time is allotted for the initial notification of the insurance company (or bank) - within a couple of days, sometimes a little more, depending on the event (insured event). It is important to meet the allotted deadline, and even better - apply immediately. Under no circumstances should you delay your application, and it is advisable to do this personally or through a proxy.
When contacting in person or in response to a notice, the insurance company will most likely offer to prepare and submit documents confirming the occurrence of the insured event, if they were not included in the notice. It is not difficult to prepare documents. For example, if you lost your job, it is enough to provide a copy of the order or other document from the employer confirming the fact of dismissal and its basis. In case of illness or accident, medical documents are provided, and in the event of death of the insured borrower, a corresponding certificate is provided.
 During the period of time established by the regulations of the insurance company, the circumstances that gave rise to the application for insurance compensation are checked. Deadlines vary. As part of such a check, the insurance company determines the existence of an event, its confirmation (proof) and the possibility of recognizing this event as an insured event with a decision on payment of compensation, its amount or refusal to pay in full or in part. The policyholder is notified in writing of the decision made. In case of complete refusal or limitation of payment, the grounds for making such a decision must be indicated. Study these grounds carefully, preferably with the assistance of a lawyer.
During the period of time established by the regulations of the insurance company, the circumstances that gave rise to the application for insurance compensation are checked. Deadlines vary. As part of such a check, the insurance company determines the existence of an event, its confirmation (proof) and the possibility of recognizing this event as an insured event with a decision on payment of compensation, its amount or refusal to pay in full or in part. The policyholder is notified in writing of the decision made. In case of complete refusal or limitation of payment, the grounds for making such a decision must be indicated. Study these grounds carefully, preferably with the assistance of a lawyer.
The most common reason for a complete refusal to pay insurance is the non-recognition of the event as an insured event. There are many reasons that can be given, and they vary depending on the situation. As a rule, this is due to the fact that in the terms of the contract, insured events are given without specifics, in the form of general formulations, or the issue of recognition/non-recognition of an event as insured depends on a number of related factors and conditions.
For example, the borrower may consider his dismissal an insured event under any circumstances, while the insurance company will most likely refuse payment, citing the fact that the dismissal occurred at his own request or for disciplinary misconduct, and this is considered as a limiting condition specified in the contract . There are also cases when the borrower's disability is not recognized as an insured event, even if it is expressly designated as such in the contract. Here, when refusing, the argument is often made that the policyholder knew about his illness at the time of signing the contract and did not inform the insurance company about it when filling out the questionnaire.
If the insurer refuses to pay insurance, without recognizing the case as insured, it is useless to argue - it is more effective, as practice shows, to immediately transfer the issue to the trial. It is unlikely that the insurance company will change its decision, even if you additionally submit a huge package of supporting documents. And you will only lose time and money in a dispute with the insurer, since the bank will not relieve you of the obligation to repay the loan while you deal with the insurance. To comply with the formalities, it is enough to prepare and send a written claim to the company demanding the fulfillment of obligations under the insurance contract in full.
At the initial stage, a written claim is sent in the following cases:
- failure to receive any response from the insurance company within the prescribed period to the appeal regarding the insurance payment;
- agreement with payment, but its delay or incompleteness;
- refusal to pay compensation in full (partial compensation).
Along with the claim, you can file complaints about the insurance company violating your financial rights. There are two main options here - Rospotrebnadzor (the most popular) and the Bank of Russia (the main insurance supervisory authority). In these cases, achieving insurance payment is a small probability, but such a step can put some kind of pressure on the insurance company, and if a positive decision is made on the complaint, it will become additional evidence that you are right. You can also file a complaint with the Interregional Union for the Protection of Insured Rights, a specialized organization that provides legal assistance, although not free.
If none of the options for pre-trial dispute resolution help, you will have to file a claim in court. In this case, the claim is made by the borrower-insurer, but in favor of the bank, which is the beneficiary in the credit insurance system. In your favor the borrower may require:
- recognize the event as an insured event (mandatory, if this is precisely the reason for the refusal to pay);
- to recover compensation for moral damages, interest for the insurance company’s use of other people’s funds, as well as court costs and expenses for legal assistance.
If an insurance company and a bank are involved as defendants, which is usually done to solve an additional problem - termination of the loan agreement, then the requirements might look like this:
- recognize the event as an insured event;
- recognize the refusal to pay insurance as illegal;
- oblige the insurance company to fulfill its obligations under the contract in full by paying compensation to the bank;
- oblige the bank to repay the loan debt at the expense of the insured amount;
- recognize the loan agreement as terminated, and if there is collateral, recognize it as terminated.
Specific requirements depend on the situation, the grounds for refusal to pay insurance, and the goals that the borrower or his heirs plan to achieve. It is important to take into account that you will not only have to prove your case, but also refute the arguments of the insurance company, and often the bank, which may side with the main defendant.
The settlement of insurance cases under compulsory motor liability insurance often raises many questions, especially when controversial situations arise with insurance companies that refuse to recognize certain cases as insured. In this article we will try to analyze in detail in what situations the driver has the right to count on compensation for damage under the MTPL policy, which cases are insurable and which are not, and what legislative norms govern this.
What law governs compulsory motor liability insurance?
Due to the fact that compulsory MTPL insurance is regulated by the relevant Federal Law No. 40 of April 25, 2002, all basic principles and concepts are recorded and documented in it. This also applies to information about the conditions for the occurrence of an insured event and its recognition as such. Therefore, if any controversial situations arise, you should refer to this document.
Summarizing the main provisions of this law, we can draw the following conclusion:
Insured events are all events in which a citizen, having a valid MTPL policy in hand, while driving a vehicle, caused harm to the life or health of other persons or the property of these persons. If such an event occurs, the company is obliged to compensate for the damage caused.
At the same time, the law also specifies an extensive list of events that are not insured events and the occurrence of which is not covered by the policy.
The version of the law dated July 3, 2016 provides for a maximum amount of compensation of 400 thousand rubles for compensation for damage to property, and 500 thousand rubles for damage to life and health.
Criteria for recognizing an event as insured
According to the above-mentioned law, an insured event under compulsory motor liability insurance occurs when two main conditions are met:
- The presence of the culprit of the accident, in respect of whom such a concept as civil liability will apply. Accordingly, there must be at least two participants in the accident: the culprit and the victim (who will be compensated for the damage by paying him compensation from the insurance company). Here are examples of relevant insurance and non-insurance events for this situation:
Insured event: The driver was distracted and did not have time to brake in front of a pedestrian crossing, which is why he crashed into a car in front.
Non-insurance event: A citizen, leaving a shopping center, discovered a dent in the trunk of his car. There were no witnesses to the incident, as a result of which the culprit of the incident was not identified.
- The damage must have occurred when the culprit used an insured vehicle (VV). According to the law, such use is recognized as driving a vehicle associated with its movement on roads and adjacent territories on which the vehicle is intended to move. Here are examples of relevant insurance and non-insurance events for this situation:
Insured event: A dump truck drove past a car parked in a parking lot and accidentally crashed into it.
Non-insurance event: Poorly secured construction material fell out of a parked truck and damaged a neighboring vehicle. The fact that the truck was moving was not recorded, and, therefore, it is pointless to expect that the insurance company will cover the damage.
What cases are not covered by insurance?
According to Article 6 of the above-mentioned Law “On Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance”, the following events are not recognized as insurance:
- causing damage while driving a vehicle other than that specified in the MTPL policy. Insurance is issued exclusively for the vehicle, and not for its owner;
- causing harm by cargo, the transportation of which is associated with risk. Such cargo must be insured separately by the owner;
- moral damages and lost profits incurred by the victim in an accident (estimated income that could have been received if the accident had not occurred);
- causing harm by a vehicle at competitions, during training driving and in other circumstances of this kind, occurring in places specially designed for these actions;
- causing damage to the life or health of citizens who are in the performance of their work duties in the case where such damage is compensated by a separate type of insurance (social, individual);
- the occurrence of other situations in which damage to the vehicle or property of the victim was caused directly by the driver of the vehicle;
- damage caused during loading and unloading operations;
- causing losses to the employing organization if an employee of this organization was injured on a vehicle (for which the policy was issued);
- Damage caused to historical and cultural values (architecture, antiques, etc.), cash, jewelry is compensated not by the insurance company, but directly by the culprit of the accident, usually in court.
Is it possible to have an insured event without an accident?
From the content of the Law “On Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance” it follows that if the fact of an accident has not been documented, then you should not expect that the insurance company will pay anything. As noted above, the case must be traffic related. If there is a need to insure a vehicle against all kinds of risks not related to accidents on the road (natural disasters, theft, fire, spontaneous combustion and other troubles), you must also take out a CASCO policy.
However, there is one exception to this situation. Many companies like to impose additional services on the client, one of which is damage insurance and theft insurance programs. Therefore, if the client decides to additionally include one of these programs in the policy, then, of course, upon the occurrence of the stipulated insured event, he will be paid monetary compensation.
Does OSAGO apply in courtyards and parking lots?
Many car owners are interested in the question: will the policy be valid if an accident occurs not while driving on the road, but in the parking lot or yard where the car was left? According to the content of the law, courtyards and parking lots are areas adjacent to the road, which means that exactly the same rules apply regarding incidents that occur there.
It should be remembered that for these territories there are standard requirements for documents submitted to the insurance company to receive payment. Getting into a serious accident in a parking lot is difficult and is mostly limited to minor accidents with minor damage. Given this fact, drivers often do not want to spend too much time on paperwork, make many mistakes in the documents, and ultimately the injured party is left without monetary payment.
In addition, accidents often occur in parking lots due to inattention, even when the cars of both the victim and the culprit are not in motion at all. A typical situation of this kind is careless opening of car doors, leading to damage to a nearby car. This incident is not an accident, which means the Law “On Compulsory Motor Liability Insurance” will not apply to it.
Is it possible to repair a bumper under OSAGO or replace it?
After an accident has occurred and the victim has contacted the insurer with documents for damage compensation, the company must assess the condition of the car after the accident. Based on the examination, a conclusion is made on the recommended course of action - in this context, repairing the bumper or replacing it. Of course, the amount of payment will depend entirely on the expert’s conclusion. Repairing the bumper will obviously cost insurers less, so there are often cases when the assessment of the car’s condition is biased. In such a situation, you need to apply for an examination to another organization, and transfer the resulting conclusion with the cost of repairs to the insurance company. If the organization does not want to pay the specified amount, then there is only one way out - to go to court.
It should be remembered that the modernization and tuning of the car must be officially registered, otherwise there is a possibility that compulsory motor liability insurance will not cover losses. For example, if a car crashes into the back of another car and causes an accident. At first glance, the case is clearly an insurance case. But when registering an accident, it turns out that the stylish bumper on the car is not original, and this modernization has not been registered in any way. As a result, driving such a car may be considered illegal, and the incident may be considered uninsurable. Accordingly, no compensation can be expected in such a situation. And this regulation applies to all parts and components of the machine that are not included in the basic configuration.
Conclusion
Insurance and non-insurance cases under compulsory motor liability insurance are enshrined in law and compensation for damage is carried out only in accordance with the norms of legal acts. Under compulsory motor liability insurance, the insurance company provides compensation only in the event of an accident, while minor accidents in parking lots or in the courtyards of houses also qualify as insured events.
In 2016, we leased a car from the Europlan company and, of course, it was insured by the Europlan insurance company under CASCO. Now the car has been involved in an accident. The culprit is our driver. The victim is our employee, a passenger. We provided to the UK, in...
How to force the insurance company to pay for compulsory motor liability insurance?
Hello, I was in an accident, I was definitely the culprit. We decided to act according to the European protocol, since the amount is small. After the incident, the next day it turned out that the victim’s insurance policy was not valid at the time of the accident, and my insurance company refused...
900
price
question
the issue is resolved
What is the best algorithm to follow in the event of an insured event under compulsory motor liability insurance, taking into account that I am the victim?
Good afternoon. I had a small accident - in the parking lot another car (Range Rover Evok), moving in reverse, collided with my car (Mazda CX-9). Everything was registered through the traffic police, all damage was indicated. The culprit has a policy dated May of this year...
700
price
question
the issue is resolved
Is it an insured event or not if the case is registered?
hello, I would like to ask, recently such an incident happened to me, I was driving a gazelle away from the loading area and the back door of the booth jumped out of its latch and hooked the nearby gazelle into the passenger door, and I called the emergency commissioners...
How to dispute an insurance company's subrogation claim?
My daughter got into an accident while driving my car. She was found to be at fault for the accident. My daughter and I are included in the OSAGO policy. Only I am included in the CASCO policy. In court, we obtained payment from the insurance company under CASCO for the repair of my car. Now the Insurance has sent...
22 July 2016, 23:55, question No. 1323154 Vadim Igorevich, St. Petersburg
Is a vehicle leaving the road an insured event under compulsory motor liability insurance?
Good afternoon Please tell me about this question: There was an accident. There was no other participant in the accident, the car simply skidded and flew into the ditch. Is this road accident an insured event under MTPL?
Does the insurance company pay under compulsory motor liability insurance for personal injury if the culprit of the accident is not identified?
those. no one is to blame, the case is dropped (the testimony of witnesses on both sides is opposite, the record from the recorder does not reflect the picture of the accident). Within what amount? In such cases, the insurance company pays 50% of the maximum amount of payment for damage to the car...
The building was damaged in the accident. Is the case insurable under MTPL?
The car was moving in reverse and collided with the front door of the store. The accident was registered by traffic police officers. The store owner filed a lawsuit against the culprit for reimbursement of the cost of the door. Is the case insurable under MTPL? The magistrate's court refused...
June 14, 2016, 09:27, question No. 1283474 Fanil Idrisov, Chelyabinsk
Distribution of compulsory motor liability insurance upon the occurrence of an insured event
Hello. We need your advice. This is the situation: an accident occurred with my participation, in fact I am the culprit - I was making a turn leaving the main road onto a secondary road, I did not notice the motorcyclist and a collision occurred, all participants are alive...
June 10, 2016, 09:59, question No. 1280653 Alexander Yurievich, Mednogorsk
How to determine an insured event under MTPL?
Question about Osago! Is this an insured event? The car was parked near the house, a tree fell on it, and there was damage to the roof of the car. The tree itself is referred to the Remontnik management company. The wood is rotten, photographs confirm this. The district police officer and staff...
Insured event under compulsory motor liability insurance, am I entitled to payment?
My car was parked in the yard. The truck responsible for the accident, moving in reverse, broke my window with an oversized load sticking out of its body. Am I entitled to a payment under compulsory motor insurance?
OSAGO, Europrotocol, Regression
Hello, question about compulsory motor liability insurance, European protocol, regression. 4 months ago there was a minor accident. I was the culprit of the accident, they drew up a European protocol and parted ways with the victim. Visible damage is minor, but the culprit's car has stopped...
















