Development of the gastrointestinal tract. Infrastructure development
Topic 4. General characteristics of the housing and communal services management system at the municipal level
SECTION 2. Economics of housing and communal services
The housing and communal services complex includes enterprises and organizations, regardless of the form of ownership, departmental affiliation, any organizational and legal forms of management, carrying out various types of production and economic activities aimed at supporting the life support of the municipality through the provision of necessary housing and communal services. Housing and communal services facilities are buildings, utilities, structures and technological links of the production cycle (housing and non-residential stock and engineering infrastructure facilities; water supply and sewerage facilities, heat, electricity, gas supply, utility networks, etc.).
The peculiarities of the housing and communal services are determined by its social and economic significance, as well as the complex system of relationships between business entities and consumers of services, primarily the population.
The social significance of housing and communal services is to create the necessary conditions for comfortable and safe living of citizens in the city [in a healthy home].
The economic importance of housing and communal services is determined by constant consumer demand for work and services and high potential for the development of private business.
Housing and communal services are a complex system of socio-economic relations, interests and interaction between state authorities and local governments, enterprises and organizations, business and the population as consumers of housing and communal services.
Housing and communal services include a wide range of activities for managing a diversified municipal economy and is divided into three sectors. The first is a housing complex, the goals and objectives of which are to ensure the normal operation of residential and non-residential real estate (consumer services, retail and office buildings, leisure facilities, educational institutions, cultural and educational institutions, health care institutions, etc.) . The second is a communal complex that produces and supplies the necessary resources (water, heat, electricity, gas) to provide comfortable living conditions. The third is an improvement complex that carries out all types of work to ensure the required level of improvement of the urban environment (construction and maintenance of city highways and bridges, landscaping, gardening maintenance, sanitary cleaning, recreation, etc.) and the provision of special services ( ritual services for the population).
In terms of creating a competitive environment, the housing complex is the most attractive, although the development of competition is hampered by the existing structure of housing management.
The utility complex is characterized by the monopoly position of most enterprises in local markets, as a rule, within municipalities, which is due to technological features and conditions for the formation of life support systems for territories associated with the network supply of resources. At the same time, in the field of natural monopolies there are certain opportunities for the formation of a specific environment in certain technological segments of production and the provision of relevant public services (repair of equipment and facilities, purchase of materials and fuel, etc.) on the basis of competitive attraction of organizations -executors of various organizational and legal forms of management.
The improvement complex combines elements of potentially monopolistic and potentially competitive sectors (sanitary cleaning, collection and disposal of household waste, landscaping, landscaping)
Management of the housing stock and its life support systems, in accordance with current legislation, is the responsibility of local governments.
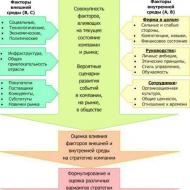
When developing a strategy for the development of the city's housing and communal services, one should take into account the interconnected system of goals, objectives and their distribution between various structural elements, which are in certain connections and relationships with each other.
The main goal of the functioning of housing and communal services can be formulated as providing an effective mechanism for the sustainable and reliable functioning of life support systems for the population, improving the quality of housing and communal services in combination with optimizing costs and ensuring social protection of the population.
Achieving this goal is based on the following principles:
- ensuring the quality of decision-making with minimal risk in the provision of housing and communal services to the population;
- provision of high-quality housing and communal services to the population - as the main customer and consumer through a system of contractual relations;
- formation of social protection programs for the interests of the population to provide benefits and subsidies in accordance with the established procedure;
- application of the principles of public-private partnership (concession) for risk management between housing management organizations, housing utility providers and municipal authorities in order to improve the efficiency of their activities;
- demonopolization of housing and communal services enterprises and creation of conditions for the development of competitive relations;
- ensuring transparency and controllability of financial flows in the management of housing organizations and enterprises supplying housing and communal services, etc.
The objectives of the management system in the housing and communal complexes of the municipality are:
- planning and implementation of a set of measures to ensure established standards of operation and maintenance of facilities and the quality of housing and communal services;
- development and approval of tariffs for certain types of housing and communal services;
- determination of strategies and programs for housing and communal services reform;
- the formation of a competitive environment in the housing and communal services sector, including on the basis of division of functions and a system of contractual relations among housing management organizations and service providers;
- creation of favorable organizational, economic and legal conditions for the development of self-government of citizens and the effective functioning of homeowners' associations and registration of condominium properties as a single complex of real estate, including land plots;
- organizing a center for housing subsidies, taking into account the projected increase in the number of citizens applying for subsidies in the process of reforming the housing and communal services;
- participation in the development of programs for updating existing built-up areas, including reconstruction and major repairs of the housing stock to ensure safe and functionally appropriate living conditions for people in a healthy home.
A quantitative assessment of the achievement of the degree of implementation of the set goals and objectives of the improvement complex is determined through regulations or standards, using appropriate methods for assessing the technical condition of road surfaces, compliance with environmental standards for sanitary cleaning of territories and waste disposal. The regulatory system for established standards should include:
- the level of technical condition and volumes of maintenance of the territory of the municipality in accordance with the requirements (in relation to the total area of the territories, separately for highways, driveways, intra-block territory);
- assessment of the quality of the sanitary condition of territories - is defined as the ratio of a time period (month, week) to the total annual (quarterly) time at which the condition of squares, streets, driveways, etc. complies with sanitary standards;
- volume of household waste to be processed (liquidation, disposal);
- the size of the green area (determined by the ratio of the actually achieved level to the standard level, at which the condition of compliance with the quality requirements of green spaces is ensured).
These indicators can also be used to justify standards for illumination of territories, standards for the maintenance of recreational areas, and the development of hotel and bath-laundry facilities.
The tasks of municipal management of the utility complex must be solved taking into account the characteristics and capabilities of local government to form a local budget on the principles of self-financing. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure the maximum required standards and standards of service, taking into account balanced resources and the availability of financial resources. The main conclusion follows from this: an important area of activity for local governments is to expand the financial base of the municipality by generating income from the use of secondary resources in waste processing, creating waste-free technologies for sanitary cleaning of territories, providing additional services, etc. d.
Increasing the efficiency of management of the utility complex should be ensured by improving organizational support, creating an indicative economic planning mechanism and a system for regulating measures to achieve established standards and quality standards, introducing modern technologies, technical systems and equipment to reduce unit costs when carrying out works The basic principles of state and municipal housing and communal services policy are:
- accessibility of housing and utilities (covering part of the costs of maintenance, repair or construction of housing, provision of utilities at the expense of the state;
- development, implementation and support of various credit and financial mechanisms for the acquisition, reconstruction and major repairs, housing construction);
- high quality of housing (in terms of architecture, quality of building materials and finishing, as well as quality of maintenance, service and management);
- market competition (between private management organizations, for financial assistance from the federal government and municipalities, for the favor of residents, for loans from commercial banks, for investments from the population, etc.);
- versatility and equality of models for the construction, acquisition, maintenance and management of housing (shared ownership, joint ownership, private ownership; various organizational forms of financing);
- control of residents, public participation in the budget process of the municipality (information, consultation, joint decision-making, partnership, and depending on management models, varying degrees of involvement of residents in management are provided - from participation in the work of governing bodies, starting with rights advisory vote, until full self-government).
The task of the municipality is to ensure that all its residents, regardless of income level, are provided with high-quality housing and communal services. The quality, volume, and range of services provided must comply with existing social norms and standards. Control over the quality of housing and communal services provided to consumers (for example, compliance with the standards of supplied water, etc.), and the development of criteria for assessing the activities of enterprises and organizations to provide these services should be carried out by the municipality. Quality indicators should be taken into account when assessing the activities of a housing and communal services enterprise and the allocation of subsidies. Of particular interest is the group of housing and communal services services that the population uses free of charge. These are road and bridge services, landscaping, urban lighting, etc.
Another important area of activity in matters of regulation of housing and communal services is monitoring compliance with consumer rights in matters of payment for industry services. Most housing and communal services enterprises are monopolists in their field, which requires special control over prices and quality.
The maximum allowable share of citizens' own expenses for housing and utilities is set annually in the amount relative to the total family income. Compensations (subsidies) for housing and utilities should be provided by local administrations through their respective structures, and not by enterprises providing these services.
Up to 70% of the budget of the average Russian family consists of food costs. Therefore, the function of local authorities to ensure social protection of the population in the provision of housing and communal services is extremely important.
Local government bodies are directly responsible for planning, development and ensuring the activities of municipal housing and communal services facilities. The existing housing stock and its infrastructure, including urban amenities, require large investment costs both for renovation and new construction, and for maintaining real estate in proper condition. In addition, in the electric power industry, water supply and sewerage services and some other sub-sectors of the housing and communal services, additional capital investments are needed to create reserve capacities (costs, as a rule, are made both at the expense of the state and at the expense of the municipality).
This necessitated the decentralization of management and the development of self-sufficiency of territories. As a result of the redistribution of rights and responsibilities, territorial authorities received more rights and opportunities to resolve issues of local importance, including the development of housing and communal services. At the same time, the functions and tasks of local authorities have become noticeably more complicated, since now they must rely on their own territorial resources.
Methods for formulating a strategy and mechanisms for implementing the housing and communal services reform program in a municipality should take into account the main provisions of the “Subprogram for reform and modernization of the housing and communal services complex of the Russian Federation” adopted in 2001 by the Government of the Russian Federation as part of the federal program “Housing”:
- ensuring the financial recovery of housing and communal services enterprises on the basis of inventory, restructuring and debt liquidation;
- refusal of direct subsidies for housing and communal services to housing and communal services enterprises and transition to a new model of economic relations based on the creation of a legal framework;
- to transfer budget resources intended for subsidies from utility companies in the industry to the disposal of citizens and change the organizational and legal forms of municipal unitary enterprises;
- organizing the transfer of budget resources intended for subsidizing housing and communal services enterprises from housing and utility companies to personalized social accounts of citizens;
- improving the social protection system for the population, taking into account the share of expenses for housing and communal services in the total family income;
- separation of functions of the owner, manager of the municipal housing stock and contractors on the basis of contractual relations;
- transfer of municipal housing stock from the balance sheet of municipal unitary enterprises to the balance sheet of the municipal customer service or to the treasury;
- abolition of VAT benefits for the population when paying for housing and communal services;
- organizing the transfer of functions for payments for housing and communal services to unified cash settlement centers that have a specialized information base;
- implementation of a unified federal tariff policy;
- attracting investments in housing and communal services, mainly on a borrowed basis (with partial budget co-financing).
The transition from state ownership to private ownership, with its diversity of organizational and legal forms, has radically changed the system of housing stock management. Various business entities participate in the housing and housing services market. Municipal authorities must know their interests and take them into account in their policies, create conditions that would interest the end result of all participants in the process of housing and communal services at all stages of the life cycle of a real estate property, including the maintenance and repair of housing stock and systems his life support. The main participants are: the municipality, the population (the consumer of housing and communal services and at the same time the owner of privatized or purchased housing), enterprises and organizations - performers of housing and communal works and services and a new structure - the housing management organization, which should become the main link a link between municipal authorities, the population and providers of housing and communal services (works).
Each municipal entity must have a financially, economically and socially justified program for reforming the housing and communal services sector, taking into account the local situation, territorial characteristics and the degree of development of the housing and communal services market.
At the municipal level, the creation of an effective management system in accordance with the requirements of market relations is considered as the highest priority task in the context of housing and communal services reform, including the formation of organizational management structures that are adequate to the requirements of market methods, with justification of rational options for municipal management and regulation.
GOVERNMENT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
1. Approve the attached Federation Strategy for the period until 2020.
2. Recommend that government bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local self-government bodies be guided by the provisions of the Strategy approved by this order when developing regional target programs and other documents, including legal acts, in the field of housing and communal services.
Chairman of the Government
Russian Federation
D.MEDVEDEV
Approved
by government order
Russian Federation
dated January 26, 2016 N 80-r
STRATEGY
DEVELOPMENT OF HOUSING AND COMMUNAL SERVICES IN THE RUSSIAN
FEDERATIONS FOR THE PERIOD UNTIL 2020
I. Introduction
The strategy for the development of housing and communal services in the Russian Federation for the period until 2020 (hereinafter referred to as the Strategy) was developed in accordance with the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Federal Law "On Strategic Planning in the Russian Federation", targets and tasks defined in the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated May 7, 2012 N 600 “On measures to provide citizens of the Russian Federation with affordable and comfortable housing and improve the quality of housing and communal services.”
The strategy was developed to:
determining the main priorities, medium-term goals and objectives of state policy in the field of housing and communal services;
formation of common guidelines and expectations among participants in legal relations in the field of housing and communal services, investors, consumers of resources and housing and communal services regarding the directions and prospects for the development of housing and communal services;
determining the main measures and activities aimed at achieving the intended goals.
The implementation of the Strategy depends on the macroeconomic situation, including price dynamics, interest rates on loans, income levels, as well as social and political factors, regional and local socio-economic conditions and characteristics.
The key directions of the Strategy are:
the formation of active and responsible owners of premises in apartment buildings who have all the rights to make decisions regarding their home and real opportunities to exercise these rights, as well as a certain level of responsibility for decisions made;
development of entrepreneurship, strengthening the competitive environment and attracting private investment in the housing and communal services sector;
improving the system of relations between owners of premises in apartment buildings, management organizations and resource supply organizations;
increasing the energy efficiency of the industry.
The sphere of housing and communal services includes the following main areas:
carrying out activities aimed at improving the living conditions of citizens in the housing stock, including the management of apartment buildings, major repairs of common property in apartment buildings, including the modernization of elevator equipment, as well as the relocation of citizens from emergency housing stock;
implementation of regulated activities in the field of supply of municipal resources (provision of public services) (issues of electricity and gas supply are considered in other strategic planning documents), including cold water supply, sewerage, hot water supply, heat supply, as well as the management of municipal solid waste;
maintaining a state information system for housing and communal services, which includes such areas as social policy, personnel policy, as well as public control.
The strategy defines the following as priorities for the development of the housing and communal services sector:
provision of high-quality housing and communal services to consumers in order to provide citizens with comfortable living conditions;
the presence of a balance of interests of various participants in the sphere of housing and communal services.
The rights, legitimate interests and obligations of all participants in the sphere of housing and communal services (resource supply organizations, consumers, persons managing apartment buildings or providing services (performing work) for the current maintenance of common property in an apartment building) must be clearly formulated and ensure accounting and development interests of all participants in legal relations in the field of housing and communal services. It is necessary to create economic prerequisites for the stable activities of each such participant, allowing it to conduct break-even activities while complying with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation;
ensuring environmental friendliness (environmental protection and protection, development and use of alternative energy sources, careful use of public resources, raising energy efficiency standards).
The strategy is the basis for the development of the Housing and Communal Services Development Strategy until 2030.
II. General characteristics of the current state of housing and communal services
Housing and communal services are one of the basic sectors of the Russian economy, providing the population with vital services, and industry with the necessary engineering infrastructure. The annual turnover in the housing and communal services sector exceeds 4.1 trillion. rubles, this is more than 5.7 percent of Russia's gross domestic product.
According to the Federal State Statistics Service, the volume of housing stock in the Russian Federation is 3.3 billion square meters. m, including apartment buildings - 2.4 billion sq. m. m (which is 72 percent of the total housing stock).
According to a survey conducted in May 2015, the majority of citizens (55 percent) consider the amount they pay for utilities to be unfair, 63 percent of respondents called the cost of utilities overpriced, while residents of small towns with population from 50 to 100 thousand people (75 percent).
At the same time, 83 percent of respondents have a positive attitude towards the installation of metering devices. In order to reduce the overall payment for consumed utility resources, the vast majority of respondents (71 percent) have already installed water consumption meters.
According to the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare, only 62.1 percent of the population in Russia consumes high-quality water. In the field of water supply, only 55.5 percent of the water supplied to the network is purified to the standard level, and in the field of water disposal and wastewater treatment, only 45 percent of wastewater is purified to the standard level. 48 percent of the population have interruptions in the supply of hot water, 42 percent of the population - cold water, and 28 percent of the population - electricity.
At the same time, according to research conducted in May 2015, more than half of the respondents began to satisfactorily assess the quality of public services, and 12 percent of respondents noted an improvement in their quality, mainly residents of small towns (20 percent) and villages (15 percent) .
According to a survey conducted by the All-Russian Center for the Study of Public Opinion in 2015, the greatest dissatisfaction of citizens is associated with the unsanitary condition of stairs and irregular cleaning of the entrance (38 percent), poor condition of roofs, walls and ceilings (36 percent), rotten and faulty water and sewer pipes ( 33 percent), unsanitary condition of basements (27 percent), malfunction of doors, window frames, balconies (24 percent), frequent breakdowns of elevators (11 percent).
According to expert estimates, the annual investment needs of the utility sector amount to at least 500 billion rubles (more than 200 billion rubles - investments in the heat supply sector, more than 100 billion rubles - investments in the water supply sector, more than 100 billion rubles - investments in the sanitation sector) .
At the same time, the housing and communal services sector has a huge potential for increasing efficiency, which, according to expert estimates, reaches 40 percent, but it can only be used if there is an influx of investment and the use of the most effective technologies.
III. Main priorities, goals and objectives of the state
policies in the field of housing and communal services
The main goals of state policy in the field of housing and communal services in accordance with Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 7, 2012 N 600 “On measures to provide citizens of the Russian Federation with affordable and comfortable housing and improve the quality of housing and communal services” are to improve the quality of life of the population by improving the quality and reliability of housing and communal services, as well as ensuring their accessibility to the population.
The priorities of state policy in the housing and communal services sector are:
improving the comfort of living conditions, including ensuring the accessibility of apartment buildings for people with disabilities and other groups of the population with limited mobility;
modernization and improvement of energy efficiency of housing and communal services;
transition to the principle of using the most effective technologies used in the modernization (construction) of municipal infrastructure facilities and modernization of the housing stock.
The concepts of quality and reliability of housing and communal services include safe and favorable living conditions for citizens in apartment buildings and residential buildings, uninterrupted provision of heating services, hot and cold water supply, sewerage, electricity and gas supply, management of solid municipal waste in accordance with sanitary standards norms and rules and other mandatory requirements established by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The main task of public authorities in the field of housing and communal services is to create a system of legal regulation that ensures the effective functioning and sustainable development of housing and communal services, including the reduction of administrative procedures and the prevention of corruption.
The implementation of this task is impossible without increasing the transparency of information about the activities of organizations in the field of housing and communal services for consumers, investors and regulatory authorities, which is ensured by the creation of a state information system for housing and communal services.
It is necessary to stimulate the development of intelligent systems for integrated metering of utility energy resources, allowing, first of all, to ensure remote metering of utility energy resources (services), including through a gradual change in the requirements for metering devices, generalization and popularization of the best solutions on this issue, as well as the creation at the regional level a single information resource (database) that ensures the organization of regular collection and systematization of reliable and up-to-date information about utility infrastructure facilities, their technical and economic condition and property rights to the above-mentioned facilities, and about regional consumers of utility resources (services). Increasing information transparency in this area will have a positive impact on the quality of management decisions, increasing energy efficiency and payment discipline, as well as helping to attract investment into the industry.
To ensure balanced development of public utility infrastructure systems, taking into account future needs, territorial and investment planning mechanisms must be coordinated.
In the context of deteriorating macroeconomic conditions, it is necessary to make maximum use of internal reserves for the development of housing and communal services related to the optimization of current and investment costs and energy saving. One of the important areas for increasing the energy efficiency of housing and communal services is the development of the energy services market.
To ensure the modernization of investment-unattractive housing and communal services facilities, it is necessary to take special measures aimed at stimulating the consolidation of assets of enterprises controlled by executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments at the level of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation with their subsequent transfer to management of private operators on the basis of concessions agreements.
To achieve the strategic goal and solve the assigned tasks, it is necessary to implement measures and activities aimed at:
development of entrepreneurship, including the development of competition, attraction of private investment in the housing and communal services sector on market conditions;
improving the quality of public administration, including optimizing the division of powers and responsibilities, improving the system of government regulation;
increasing the efficiency of infrastructure management, stimulating energy saving, while taking into account the problem of negative economic efficiency of most projects to increase the energy efficiency of municipal infrastructure facilities and their high cost;
transition to the use of the most effective technologies used in the modernization (construction) of municipal infrastructure facilities;
the formation of a motivation system for participants in legal relations in the field of housing and communal services, both in the housing and public utilities sectors, stimulating them to rational and energy-efficient behavior;
ensuring targeted social support for the population;
development of human and social capital, including increasing labor productivity, developing scientific and technical potential, improving the system of public control, improving the image of housing and communal services in the media.
The strategy defines the goals and objectives of state policy in certain areas of the housing and communal services sector, taking into account their specifics, as well as the measures and activities necessary to achieve the goals established in these areas and solve the assigned tasks.
The qualitative and progressive development of the housing and communal services sector will serve as one of the main sources of economic development of the regions of the Russian Federation due to the close connection of the industry with more than 30 related industries. During periods of financial instability, the housing and communal services sector is one of the most stable sectors of the economy of the Russian Federation (including due to the presence of guaranteed demand for the goods, works and services produced).
Achieving the set goals and objectives, as well as implementing the measures provided for by the Strategy, will lead to the creation of a balanced (between consumers and producers of housing and communal services) model of relations in the field of housing and communal services, which will be based on the following target situation - providing consumers with quality housing -utilities, the cost of which, on the one hand, is available to the consumer (including taking into account the provision of state (municipal) support to socially vulnerable categories of the population), and, on the other hand, provides not only reimbursement of the costs of producing these services to their producers, but and returns for investors.
Monitoring the achievement of goals and solutions to the objectives of the Strategy will be carried out by the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation through the use of the following main tools:
state information system of housing and communal services in terms of information posted in this information system;
information departmental system for monitoring the state of housing and communal services of the Ministry of Construction of Russia;
automated system "Housing and Communal Services Reform", currently administered by the state corporation - the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services, regarding issues of relocation of citizens from emergency housing stock and the functioning of regional capital repair systems.
Based on the results of monitoring the implementation of the Strategy, it is planned to send annual reports to the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as to consider these results at meetings of the interdepartmental working group on housing and communal services, created by the decision of the Chairman of the Government of the Russian Federation D.A. Medvedev. dated May 20, 2015 N 3083p-P9.
IV. Development measures
housing and communal services in main areas
sphere of housing and communal services
1. Management of apartment buildings
In the field of management of apartment buildings, the main goal of state policy is to increase the level of citizen satisfaction with the quality and cost of services for the maintenance and ongoing repairs of the common property of apartment buildings, as well as utilities.
Achieving this goal will be ensured by solving the following tasks:
ensuring professional management of apartment buildings, that is, management organizations licensed to carry out business activities in managing apartment buildings;
creating conditions for increasing the activity and responsibility of owners of premises in apartment buildings through the development of forms of self-government of citizens in the field of housing and communal services, primarily such as councils of apartment buildings and homeowners' associations;
creating incentives for owners of premises in an apartment building to preserve and increase the value of their property in the said building, including by ensuring its proper maintenance, as well as timely major repairs and modernization.
The main regulatory legal acts in this area include the Housing Code of the Russian Federation (as amended by the Federal Law “On Amendments to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation and the recognition as invalid of certain provisions of legislative acts of the Russian Federation”), as well as Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 28, 2014 N 1110 "On licensing of business activities for the management of apartment buildings."
Since 2015, the efforts of the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation have been aimed at organizing work related to the licensing system for business activities for managing apartment buildings, and developing fair competition in the market for managing apartment buildings.
In the first quarter of 2015, applications for licenses to carry out business activities in the management of apartment buildings were submitted by 12.5 thousand management organizations operating and managing apartment buildings as of April 1, 2015. Review and issuance of such licenses in relation to the specified organizations were completed on time. Licensing commissions issued about 11 thousand licenses, and denied licenses to 13 percent of management organizations. At the end of July 2015, 12.9 thousand licenses had already been issued, information about which is in accordance with the Federal Law "On Amendments to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation and the Revocation of Certain Provisions of Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation" placed in the state information system of housing and communal services in the unified federal register of licenses.
Licensing will free the market from unscrupulous management organizations, increase the responsibility of management organizations for the quality of housing and communal services provided, and will also provide owners of premises in apartment buildings with real tools of influence on management organizations that carry out their activities in violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation, the rights and legitimate interests of citizens .
Licensing is a mechanism for constant monitoring of management organizations and taking effective measures against business entities that commit violations. The effectiveness of this mechanism will be determined by monitoring the situation in the management of apartment buildings, including using the indicator of consumer satisfaction with the quality of services provided.
The issue of creating a professional public association of management organizations should be explored in order to form uniform professional standards for carrying out activities related to the management of apartment buildings, presenting the opinion of the professional community on current issues arising in the field of management of apartment buildings, and participating together with interested authorities in developing the necessary decisions.
The solution to the problem of forming responsible and active owners of premises in apartment buildings will be ensured, among other things, by conducting an information and explanatory campaign to raise awareness of residents of apartment buildings about their rights and responsibilities and simplify the coordination of their actions by expanding the forms of holding general meetings of owners of premises in apartment buildings .
As part of the implementation of the Strategy, proposals will be prepared to improve the legal regulation of the activities of associations of owners of premises in an apartment building (homeowners' associations, housing construction cooperatives, etc.).
At the same time, the development of activity of owners of premises in an apartment building will be facilitated by the changes adopted by the Federal Law “On Amendments to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” regarding the introduction of new simplified forms for holding a general meeting of owners of premises in an apartment building (in person and in absentia form), uniform forms and requirements for the execution of minutes of general meetings and decisions of owners of premises in an apartment building, as well as other provisions of the specified Federal Law. In order to further improve the procedure for holding general meetings of owners of premises in an apartment building and making decisions at general meetings of owners of premises in an apartment building, it is necessary to further study the issues of simplifying the coordination of actions of owners of premises in an apartment building, including participation in general meetings of owners who do not actually live in apartment building, as well as issues of simplifying the forms and methods of informing owners about meetings.
To develop a management system for apartment buildings with a high level of wear and tear, it will be necessary to create a special model for managing such buildings using various support measures from state and (or) municipal structures that provide relevant services. At the same time, state policy in the field of management of apartment buildings with a high level of wear and tear, as well as the actions of authorities in the region and (or) municipality, should be focused on attracting private management organizations to this area, without creating conditions under which they dominate in this segment market for the management of apartment buildings will be state and (or) municipal organizations engaged in business activities for the management of apartment buildings.
A new model of legal relations for payment of utilities (resources) will be formed, providing for:
improving the payment system for utility services;
increasing the responsibility of consumers for timely payment of housing and communal services, as well as the responsibility of resource supply and management organizations for the quality of public services and resources by introducing, among other things, special fines for violation of the quality parameters of services provided.
It is necessary to solve the following problems in the management of apartment buildings:
creation of a mechanism for differentiated liability of management organizations, including in terms of the amount of fines imposed on management organizations in connection with their violation of licensing requirements;
establishment of additional requirements for management organizations (requirements for authorized capital, material and technical base, financial condition, etc.), including their inclusion in the licensing requirements;
development of proposals on the need to take into account economically justified business profits when determining the amount of payment for housing services;
creating a clear and universal mechanism for checking (primarily for the owner of premises in an apartment building) the validity of the established fee for the maintenance and current repairs of common property in an apartment building (housing service consumer calculator), as well as improving the mechanism for reducing the specified fee depending on the volume and quality of the actual service provided;
clarification of the provisions of the legislation of the Russian Federation establishing the responsibility of licensing and supervisory authorities regarding the commission of corruption offenses in this area;
improving the procedures for resolving disputes when collecting debts for housing and communal services, as well as considering the possibility of simplifying such collection, including through writ proceedings;
improving the procedure for limiting the provision of utility resources (services), including simplifying the procedure for notifying the consumer-debtor about the introduction of a regime for limiting the provision of utility services, expanding the list of grounds for introducing restrictions (provision) of utility services, while excluding the possibility of abuse by resource supply organizations and unreasonable violation of the rights and legitimate interests of consumers.
One of the tasks that will be solved is to improve the legal regulation of the accounting and use of common property in an apartment building, as well as the development of effective mechanisms for its protection from unlawful actions of third parties.
Particular attention will be paid to improving state policy on the issues of updating and significant innovation of legal acts that establish technical requirements for common property in an apartment building and its maintenance, including on the formation of modern rules and norms for the technical operation of the housing stock.
This part requires:
development of measures to restore the legal rights of owners to common property in an apartment building, including on previously completed transactions, paying special attention to cases of illegal alienation by authorities of property related to common property in an apartment building;
improving the rules for concluding management agreements for apartment buildings, including tightening the requirements regarding the availability and execution of management agreements for apartment buildings, taking into account the approximate form of a management agreement approved by the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation.
In 2016, the consumption of communal resources for general household needs will be included in housing services. This solution encourages management companies to save energy and identify theft of utility resources. Together with measures to develop energy services, this will make it possible to use significant internal reserves to reduce the cost and improve the quality of housing and communal services in an apartment building, as well as finance energy-saving measures through the resulting savings in energy resources. Until this point, it is necessary to carry out work to update standards for the consumption of utility services, including for general household needs, as well as develop other measures to encourage consumers to install meters for the consumption of utility resources provided for by the Strategy.
In addition, as part of the implementation of the Strategy, proposals will be further developed to improve the payment procedure for the provision of housing and communal services, including the introduction of discounts on their payment or the determination of prepayment conditions (the procedure and mechanisms for implementation of which will be determined by the legislation of the Russian Federation), clarification of the payment period under resource supply agreements and management agreements.
The development of energy services in the housing stock (apartment buildings) will also be ensured. In particular, the procedure for concluding energy service contracts will be simplified and the possibility of fixing the volume of thermal energy consumption in an apartment building for a long-term period will be provided.
Since 2015, a system of federal control over compliance with housing legislation has been operating on the territory of the Russian Federation through the activities of the chief state housing inspector, empowered to conduct inspections of state housing supervision bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
In order to ensure additional control over the implementation of the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of management of apartment buildings, work will continue to organize and ensure the functioning of institutions of public control in the field of housing and communal services.
In addition, the following tasks will be implemented within the framework of the Strategy:
improving the mechanism for selecting and changing a management organization, ensuring, on the one hand, the protection of the rights and legitimate interests of owners of premises in apartment buildings, and, on the other hand, excluding the adoption of unfounded decisions on changing the management organization;
improving the system of information disclosure by persons engaged in managing apartment buildings, including in order to increase the awareness of owners of premises in an apartment building;
improving the housing stock monitoring system;
improving the system for metering the consumption of utility services, including through the implementation of measures aimed at stimulating consumers to install metering devices (communal and individual), and establishing liability for interference with the operation of metering devices and unauthorized connection to intra-house networks, as well as the development of measures aimed to comply with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on the inclusion of an automated system for accounting for the consumption of utility resources (services) as part of the mandatory equipment for the design and construction of apartment buildings. At the same time, as a fundamental principle for the implementation of such measures, it is necessary to identify the principle of accounting for the consumed utility resource (service) using appropriate metering devices for the consumption of utility resources and resolve the issue of ownership of such a metering device. As part of the implementation of these measures, it is also necessary to work out the issue of unifying methods for transmitting meter readings to a resource supplying organization or other organizations that provide relevant services for receiving and transmitting the specified data;
elaboration of proposals for the use as a measure to stimulate the installation of meters for the consumption of utility resources (services), calculation of the consumption of a utility resource (service) using calculation methods based on the maximum (allowed) power (load) in conditions where such a device can be installed, but the corresponding obligation is not fulfilled by the owner of the premises in an apartment building;
encouraging large-scale implementation of energy-saving measures in apartment buildings on the basis of energy service agreements (contracts), including the development of measures that encourage the use of energy-efficient materials and technologies when performing work (providing services) for the routine maintenance and repair of apartment buildings;
creation of a system for monitoring the state of energy efficiency in the housing sector, including the introduction of a classification of apartment buildings by energy efficiency level;
improving the terminology used in the housing sector, including the concepts of “apartment building”, “blocked building”, etc.;
analysis and, if necessary, updating of standards, norms and rules regarding solving issues of technical regulation of the maintenance of an apartment building;
finalizing a unified form of payment document for payment of housing and communal services, including the mandatory use of a two-dimensional bar code symbol in it in accordance with GOST 56042-2014, ensuring the possibility of receiving a receipt in electronic form if the consumer agrees, if the legislation of the Russian Federation allows the use of such types of payment, such as "autopayment".
In order to assess the achievement of the set goals in the field of management of apartment buildings, by 2016, indicators characterizing the quality of customer service will be determined, and periodic studies will be organized to assess consumer satisfaction with the level of service and quality of services in the field of management of apartment buildings.
2. Major repairs of common property in apartment buildings
In the field of capital repairs of common property in apartment buildings (hereinafter - capital repairs of apartment buildings), the goal of state policy is to create and ensure the sustainable functioning of regional systems for capital repairs of common property in apartment buildings (hereinafter - regional capital repair systems), ensuring its timely implementation, necessary quality and reasonable cost of work (services) with a gradual transition from the predominance of the system of state organization of capital repairs through the system of regional operators to the predominance and spread of the model of organization of capital repairs through a system of special accounts.
In 2014, regional capital repair systems were launched, based on financing capital repairs from the funds of the owners of premises in apartment buildings.
Currently, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation have created mechanisms that ensure long-term planning for capital repairs of apartment buildings and are based on its financing by the owners of premises in apartment buildings by paying a monthly mandatory minimum contribution for capital repairs in relation to apartment buildings included in regional capital repair programs.
According to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, in 2014, within the framework of regional capital repair programs, the renovation of 7.7 thousand apartment buildings with a total area of 37 million square meters was completed. m, in which 1.4 million people live.
The total volume of financing of regional capital repair programs in 2014 amounted to 36.1 billion rubles, including from the funds of the state corporation - the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services - 5.6 billion rubles (15.5 percent), from consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - 18.3 billion rubles (50.7 percent), at the expense of owners - 12.19 billion rubles (33.8 percent).
It should be noted that the Federal Law “On Amendments to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation and certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation” introduced significant changes in terms of adjusting the norms governing capital repairs, based on law enforcement practice and identified problems, including in terms of improving:
the procedure for the formation and updating of regional capital repair programs, including clarifying the procedure for determining the timing of capital repairs and simplifying the procedure for making changes to regional capital repair programs when such changes are caused by technical errors made during their formation;
legal regime for the functioning of special accounts;
legal status of the special account owner;
activities of regional operators.
The primary tasks of state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments for 2015 - 2016 are:
unconditional fulfillment of obligations undertaken in accordance with the approved regional capital repair programs and short-term plans for their implementation to carry out capital repairs. This is necessary, among other things, from the point of view of increasing citizens’ confidence in the operation of new capital repair systems, for which nothing can be better than demonstrating positive and real examples of the system’s operation;
completing the formation and ensuring high-quality operation of the monitoring and control system for the functioning of regional operators in accordance with methodological recommendations approved by the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation;
updating regional capital repair programs in order to eliminate identified deficiencies, as well as bring them into compliance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation;
continuation of active information and educational work with owners of premises in an apartment building on the organization of major repairs;
formation of a system for appointing managers of regional operators who meet the qualification requirements established by the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation;
practical launch of preferential lending mechanisms for capital repairs, including with government support;
development of additional measures aimed at stimulating the development of special accounts, including:
vesting the authorized body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation with the right to make a decision (in agreement with the owners of the premises and the regional operator) on the early transfer from the regional operator’s account to a special account.
The task of improving the quality of capital repairs and the efficiency of expenses for its implementation will be solved through comparative analysis at the federal level and the creation of consolidated standards for the costs of implementing standard types of work, as well as methodological support for the process of carrying out activities by regional operators. In order to ensure transparency in the bidding for the selection of organizations to carry out capital repair work, the procedure and conditions for the placement by the regional operator of temporarily free funds of the capital repair fund, formed on the account of the regional operator, will be established.
In order to implement additional measures during major repairs aimed at increasing energy efficiency, special tools can be used to finance such work on the principles of energy service.
One of the issues that deserves special attention when organizing a major overhaul is the issue of modernizing elevator equipment in an apartment building, including in order to ensure the accessibility of apartment buildings for people with disabilities and other low-mobility groups, vandal resistance, energy efficiency and fire safety of elevator equipment.
The basis of the system of state regulation in the field of elevator facilities is the technical regulation of the Customs Union TR CU 011/2011 “Safety of Elevators”, according to which, after the expiration of the designated service life (over 25 years), it is not allowed to use the elevator for its intended purpose without conducting a conformity assessment, based on the results which modernization (overhaul) or replacement of the elevator is carried out. The corresponding work should be carried out on a massive scale as part of the implementation of regional capital repair programs. This service, from the point of view of experts, is one of the most attractive for the use of credit funds for the purpose of financing it. Another measure, the implementation of which will simultaneously help solve the problem of modernizing the elevator industry and stimulate the development of domestic manufacturers, is to ensure import substitution through the use of elevators from domestic manufacturers.
To ensure the timeliness of major repairs, systematic monitoring of the use of the housing stock and ensuring its safety will be carried out through the collection, systematization and analysis of information in accordance with the established list of indicators.
For these purposes, the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation has put into operation an automated information system for monitoring the implementation by constituent entities of the Russian Federation of regional capital repair programs, which ensures:
obtaining complete and up-to-date information on the planned and (or) completed major repairs of each apartment building by any interested party;
tracking the main stages of organizing and carrying out major repairs of each apartment building included in the regional capital repair program and the short-term plan for its implementation, including ensuring the participation of the owners of premises in the apartment building and the public in the acceptance of major repairs;
monitoring the quality of planning and dynamics of implementation of regional capital repair programs;
control of the cost level of major repairs for a certain type of work (service);
identifying and eliminating duplication of inclusion of apartment buildings in regional capital repair programs and resettlement programs from dilapidated and dilapidated housing;
information openness and transparency in the implementation of regional capital repair programs.
In addition, on the official website of the Ministry of Construction and Housing and Communal Services of the Russian Federation and the portal of the state corporation - the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services "Housing and Communal Services Reform" on the information and telecommunications network "Internet" in the "Major Repairs" section within the framework of the color indication system "traffic light" displays indicators of the implementation of regional capital improvement programs.
The main risk in the functioning of the system of capital repairs of apartment buildings is its possible financial imbalance.
In order to avoid the formation of deficits and unfunded liabilities in regional capital repair funds, federal executive authorities will monitor the financial stability of regional capital repair operators and the compliance of the minimum amount of contributions for capital repairs with the volume of obligations assumed by regional operators.
In addition, at the federal level, a model will be developed that will make it possible to assess the financial stability of already functioning regional capital repair systems, predict its development and possible operational problems, and also take timely measures aimed at solving problems.
An important issue is the elaboration of proposals for the development of a unified approach to the payment of commissions for the services provided for the acceptance and transfer to special accounts of payments for contributions for capital repairs, including as regards the obligation to pay these fees.
The task of increasing the efficiency of the functioning of the established capital repair system will be solved by attracting additional sources of financing for capital repairs of apartment buildings, primarily through the development of lending for capital repairs of apartment buildings.
According to the results of a study conducted in June 2015, 61 percent of respondents see the need for major repairs in the next 3 to 5 years, while more than a third (34 percent) of respondents believe that their apartment building needs to be repaired immediately.
To expand the capabilities of citizens to carry out major repairs, including selective repairs, reduce the “waiting period” for such repairs, improve the comfort and quality of living in an apartment building beyond the minimum list established by the Housing Code of the Russian Federation, activities will continue in terms of the development and development of lending mechanisms capital repairs of apartment buildings. Owners of premises in an apartment building will be able to carry out the necessary work without waiting for the deadlines provided for by the regional capital repair program, and pay for this work through long-term loans, the repayment of which will be carried out from contributions for capital repairs, included in payments for housing and communal services . To increase the availability of such loans and ensure the involvement of a larger number of owners of premises in apartment buildings, attracting additional sources of financing for major repairs of common property, state support for such owners in the form of subsidizing the interest rate and subsidizing part of the loan itself will allow.
Also, in order to reduce commercial risks, reduce the cost of loans and increase their terms, mechanisms will be used to refinance loans issued for major repairs of apartment buildings.
The development of lending mechanisms is one of the priority tasks within the framework of the development of regional capital repair systems, and also has important social significance. The possibility of carrying out major repairs in apartment buildings using credit funds will significantly reduce the number of houses requiring major repairs and relieve certain concerns of property owners regarding the formation, preservation and use of capital repair funds.
Nevertheless, the involvement of credit institutions in the process of lending for capital repairs is constrained by a number of objective factors, in particular the risks associated with the lack of collateral for these loans. Payments by the owners of the premises, which are required by law, are considered as the main collateral for a loan for major repairs of apartment buildings. As additional security, the use of state and municipal guarantees is provided, provided that appropriate support measures are provided for in the relevant budgets.
3. Liquidation of emergency housing stock
4. Modernization of housing and communal services
Cold water supply and wastewater disposal5. Management of municipal solid waste
Hot water supply
Heat supply
6. State information system of housing and communal services
7. Social policy
8. Personnel policy
9. Public control
/full text see attached file/
V. Final provisions
The implementation of the Strategy is planned for 2016 - 2020.
Resource support for the implementation of the Strategy is carried out at the expense of budgetary and extra-budgetary sources, generated and provided for in the prescribed manner.
Target indicators for the development of housing and communal services in the Russian Federation until 2020 are presented in the appendix.
Application
to the Development Strategy
housing and communal services
In Russian federation
for the period until 2020
TARGETS
DEVELOPMENT OF HOUSING AND COMMUNAL SERVICES IN THE RUSSIAN
FEDERATIONS UNTIL 2020
Target | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
Total area of apartment buildings for which major repairs were carried out on time as part of the implementation of regional capital repair programs (thousand sq. m) | |||||
Utility fee collection rate (percent) | |||||
Volume of resettled emergency housing stock recognized as such before January 1, 2012 (thousand sq. m)<*> | |||||
Level of technological losses during transportation through networks (percent): | |||||
thermal energy | |||||
cold water | |||||
Share of the population provided with high-quality drinking water that meets sanitary and epidemiological standards in the total population provided with centralized water supply services (percentage) | |||||
Share of wastewater treated at biological treatment facilities that meet established requirements in the total volume of wastewater passed through treatment facilities (percentage) | |||||
Share of borrowed funds in the total volume of capital investments in heat supply, water supply, sewerage and wastewater treatment systems (percent) | |||||
Share of expenses for housing and communal services in total family income (percent) | |||||
Transfer to private operators, in the authorized capitals of which the share of participation of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation and (or) municipalities is no more than 25 percent, on the basis of concession agreements of housing and communal services of all state and municipal enterprises carrying out ineffective management (percent) |
///
Download:
Department of Housing and Utilities is a basic sphere of the economy that directly determines the quality of life and well-being of the population, as well as the conditions for the development of all types of economic activity. The main directions of reform changes were: transfer of the utility industry to market relations, attraction of private business, formation of the institution of an effective owner. Currently, in the territory of the Gatchina municipal district, housing and communal services enterprises operate in the field of providing housing services (Municipal Unitary Enterprise "Housing and Communal Services of the City of Gatchina", Municipal Unitary Enterprise "ZhKH" of Kommunar, Municipal Unitary Unitary Enterprise of Housing and Communal Services "Siversky", LLC "Management Company of Housing and Communal Services No. 1" and LLC "Management Company "Vozrozhdenie" in the Gatchina region) and in the provision of utilities (MUP "Heat Networks" and MUP "Vodokanal" in Gatchina, MP "ZhKS" in Kommunar, JSC "Utility Systems of the Gatchina District" in Gatchina district), which serve the entire territory of the municipality.
Currently, a number of strategic documents at the federal and regional levels have been developed that set guidelines for the reform and development of the housing and communal services sector, and a draft “Strategy for the development of housing and communal services in the Russian Federation until 2020” has been prepared. The sphere of housing and communal services includes the following main areas:
Carrying out activities aimed at improving living conditions;
Carrying out regulated activities in the field of supply of utility resources (provision of utility services).
Issues of development of housing and communal services, including the increase in tariffs for housing and communal services and problems of maintaining the housing stock are perceived by the population as the most pressing personal problems.
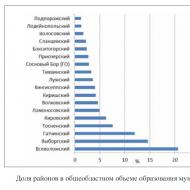
Dynamics of volumes housing construction characterized by steady growth. According to Petrostat, in 2014, a total (usable) area of 123.8 thousand sq.m. was commissioned in the Gatchina municipal district. The growth rate by 2013 was 96%. During the reporting period, 1,512 apartments were commissioned. On commissioning of the total (useful) area in 2014, Gatchina municipal district takes 3rd place in the Leningrad region.
The Gatchina municipal district is one of the largest, dynamically developing districts in the field of construction in the Leningrad region. The GMR construction complex shows stability in investment activity and volumes of commercial, industrial and residential construction. Housing construction (multi-apartment residential buildings) is most intensively carried out in Gatchina, Kommunar (low-rise residential complex), Maloye Verevo, Malye Kolpany, Nizhnyaya (low-rise residential complex “Golden Keys”, Taitskoye urban settlement), Tervolovo, Pudost (Kivennapa).
The average level of housing provision for the population in the Gatchina municipal district is quite high - 28.2 sq.m./person. In general, in the municipal district the housing stock is represented by almost 40% of individual residential buildings, and 60% by multi-apartment residential buildings. The average annual housing construction index is 101.5%. The level of depreciation of the housing stock is growing slightly (up to 46% on average for the municipal area). Officially registered dilapidated and dilapidated housing stock is within the permissible limits: it is 0.6% of the total area of the housing stock.
Table 25.
Characteristics of the housing stock
| 01.01. | 01.01. | 01.01. | 01.01. | 01.01. | 2015 as a percentage of 2011 | |
| 5919,39 | 6028,37 | 6166,72 | 6245,67 | 6272,91 | 106,0 | |
| including individual housing construction | 2260,84 | 2339,68 | 2452,44 | 2460,39 | 2455,73 | 108,6 |
| 3658,55 | 3688,69 | 3714,24 | 3785,28 | 3817,18 | 104,3 | |
| 28,1 | 28,9 | 29,1 | 29,3 | 28,19 | 100,3 | |
| 89,4 | ||||||
| 43,8 | 43,9 | 43,9 | 43,9 | 45,96 | 104,9 | |
| 20,5 | 20,39 | 18,3 | 22,54 | 20,03 | 97,7 | |
| 37,375 | 20,92 | 20,1 | 17,04 | 17,03 | 45,6 | |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | ||||||
| Total area of housing stock, thousand sq.m | 1966,5 | 1996,5 | 1999,9 | 2051,2 | 2059,38 | 104,7 |
| including individual housing construction | 162,5 | 163,2 | 161,9 | 161,9 | 161,9 | 99,6 |
| including in multi-apartment residential buildings | 1833,2 | 1889,4 | 1897,48 | 105,2 | ||
| Average level of housing supply, sq.m./person. | 21,1 | 21,2 | 20,95 | 21,3 | 21,38 | 101,3 |
| Number of citizens registered and in need of improved housing conditions, people. | 74,3 | |||||
| Depreciation level of housing stock, % | 44,03 | 41,2 | 93,1 | |||
| Emergency housing stock, thousand sq.m. | 0,755 | n/a | 1,2 | 1,2 | 2,3 | 304,6 |
| Dilapidated housing stock, thousand sq.m. | 15,229 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
The dynamics of the main parameters of engineering networks for heat supply, water supply and sanitation are presented below in Table. 26.
Table 26.
Comparative characteristics of the indicators of communal infrastructure of the Gatchina municipal district and the Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina"
| Indicator, unit of measurement | Gatchina municipal district | Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |
| Total | in % of GMR | ||
| 21,6 | |||
| including those in need of replacement and repair, m | |||
| Number of heat supply sources, units | 14,3 | ||
| 285062,4 | 41,8 | ||
| (44,9 %) | 38000 (31,9 %) | 29,7 | |
| 35,6 | |||
| including those in need of replacement, m (% of total length) | (64,4 %) | 118570 (71 %) | 39,3 |
| 31,6 | |||
| including those in need of replacement, m (% of total length) | 340785 (70,4 %) | 207 (0,1 %) | 0,1 |
Communal infrastructure characterized by a significant level of depreciation of fixed assets heating, water supply and sanitation . The outdated system of public utility infrastructure of the Gatchina municipal district does not allow compliance with the requirements for the quality of public services supplied to consumers.
The depreciation of fixed assets in the field of water supply and sanitation as of the beginning of 2014 is over 80%, including sewerage treatment facilities - more than 85%. As a result of the high degree of wear and tear of equipment and networks, the number of failures and accidents in heat supply, water supply and sanitation systems practically does not decrease, which is about 220 and 280 per year per 1000 km of networks, respectively. One of the main problems remains the lack or complete absence of modern treatment facilities in urban and rural settlements of the Gatchina municipal region. The share of wastewater treated to standard values in the total volume of wastewater passed through treatment facilities does not exceed 40%.
The lack of noticeable positive results in improving the technical condition of fixed assets and increasing the efficiency of the public utility infrastructure system is associated with an acute lack of investment.
Currently there is an insufficient level gasification of populated areas Gatchina municipal district with natural gas. As of July 1, 2014, the level of gasification with natural gas is 68.7%. Currently, the number of non-gasified settlements in the Gatchina municipal district is 177 out of 240. Gasification problems are largely due to the fact that gasification facilities - the private sector, small settlements - are located locally over a large territory. This entails significant costs for laying main and inter-settlement gas pipelines.
In order to ensure rational use of energy resources Since 2010, on the territory of the Gatchina municipal district, work has been carried out to implement the Federal Law of November 23, 2009 No. 261 - Federal Law “On Energy Saving and Increasing Energy Efficiency”.
Table 27.
| Communal sphere | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2014 as a percentage of 2009 |
| Single length of street gas network, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 152,1 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 130,1 | ||||||
| 25,2 | 21,0 | 20,2 | 20,8 | 19,4 | 21,6 | ||
| Length of heat and steam networks in two-pipe calculation, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 285062,4 | 285062,4 | 285062,4 | 98,3 | |||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 84,0 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 48,9 | 49,1 | 48,4 | 41,8 | 41,8 | 41,8 | |
| including those in need of replacement, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 104,4 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 88,3 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 35,1 | 35,5 | 32,8 | 31,2 | 31,3 | 29,7 | |
| Length of heating and steam networks that were replaced and repaired during the reporting year, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 132,5 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 96,3 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 53,6 | 37,9 | 36,4 | 37,1 | 35,3 | 39,0 | |
| Single length of street water supply network, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 156,2 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 176,1 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 31,6 | 32,9 | 27,2 | 35,8 | 35,6 | 35,6 | |
| Gatchina municipal district | 145,9 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 166,2 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 31,4 | 33,4 | 25,3 | 36,5 | 29,4 | 35,8 | |
| Single length of street water supply network, which was replaced and repaired during the reporting year, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 20,7 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 0,5 | 2,1 | 1,9 | 24,3 | 12,6 | 58,4 | |
| Single length of street sewer network, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 181,2 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 396,0 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 15,7 | 15,7 | 11,7 | 34,3 | 34,3 | 34,3 | |
| including those in need of replacement, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 178,1 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 474,1 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 15,9 | 15,8 | 13,2 | 40,1 | 40,0 | 42,4 | |
| Single length of street sewer network, which was replaced and repaired during the reporting year, m | |||||||
| Gatchina municipal district | 1231,1 | 328,1 | |||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 86,6 | ||||||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" as a percentage of GMR | 41,5 | 21,9 | 7,0 | 64,6 | 2,7 | 11,0 |
To problems related to functioning and development transport infrastructure The condition of local roads of the Gatchina municipal district (including artificial road structures, development elements) should be included. Within the boundaries of the Gatchina municipal district, the length of federal highways is 111 km, regional highways - 556 km, and local roads of the Gatchina municipal district - 150 km.
The level of quality of life of the population of the Gatchina municipal district directly depends on the condition of local roads, as the main routes providing communication with populated areas (including access to them for special equipment: fire trucks, ambulances, etc.). Therefore, the development of the road network of the Gatchina municipal region, its arrangement, solving issues of traffic management, timely repairs and maintenance is the most important task in ensuring the life and economic development of the Gatchina municipal region. An important factor is the quality of services provided to the population in the field of transportation by road and rail.
Characteristics of indicators of transport infrastructure facilities and passenger traffic in the Gatchina municipal district and the municipal formation “City of Gatchina” in the period 2012-2014. is given in the table.
Table 28.
Characteristics of transport infrastructure facilities and passenger transportation
| Territory | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 |
| Length of public roads of local importance, total (km) | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 777,3 | 1 205,80 | 1 248,20 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 154,0 | 154,0 | 154,0 |
| including hard surface (km) | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 617,6 | 1 022,30 | 1 067,70 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 153,9 | 153,9 | 153,9 |
| of which with improved coverage (km) | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 423,8 | 376,80 | 454,40 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 147,4 | 147,4 | 147,4 |
| Share of paved roads in the total length of roads, % | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 79,0 | 85,00 | 85,50 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 99,9 | 99,9 | 99,9 |
| Share of roads with improved surfaces in the length of roads with hard surfaces, % | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 69,0 | 37,00 | 42,50 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 95,8 | 95,8 | 95,8 |
| Length of public roads of local importance that do not meet regulatory requirements (km/% of the total length of public roads of local importance) | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 30,26/ 3,9 | 44,60/ 3,7 | 70,50/ 5,6 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| The volume of financial resources aimed at implementing road activities as part of the implementation of the activities of the state program of the Leningrad Region “Development of highways in the Leningrad Region”, thousand rubles. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 371379,38 | 479 576,50 | 41 329,84 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 125744,8 | 179537,5 | 2938,0 |
| Length of repaired public roads of local importance as part of the implementation of the state program of the Leningrad Region “Development of Highways in the Leningrad Region” (km) | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 14,83 | 26,81 | 8,75 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | 3,2 | 10,5 | |
| Public road transport routes providing transport services to the population and passing through the territory of the municipality, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | |||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| including: suburban services, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | |||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| including: city traffic, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | |||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| including: intermunicipal transport, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | |||
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| Rolling stock of automobile and urban ground electric transport for public use, providing transport services to the population, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 238,00 | 203,00 | |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| including on routes: suburban services, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 145,00 | 71,00 | |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| including on routes: city traffic, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 16,00 | 23,00 | |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| including on routes: intermunicipal transport, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 77,00 | 109,00 | |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| Routes of public railway transport for suburban transport, providing transport services to the population, passing through the territory of the municipality, units. | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 5,00 | 18,00 | |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | |||
| Share of transport infrastructure facilities equipped for access for people with disabilities from the total number of infrastructure facilities of suburban, urban and intermunicipal transport, % | |||
| Gatchina municipal district | 4,0 | 4,00 | 4,00 |
| Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina" | n/a | n/a | 3,8 |
In general, in terms of indicators characterizing the state of existing communication routes and the quality of transport services for the population, the Gatchina municipal district is inferior to the Municipal Municipality "City of Gatchina".
Thus, the technical characteristics of all public roads of local importance in the municipal municipality "City of Gatchina" have been brought up to standard indicators, while the length of roads of the Gatchina municipal district that do not meet standard indicators is increasing every year and, as of 2014, is more than 5% of the total length.
In 2014, the amount of funding from the regional budget allocated for road activities decreased sharply. As a result, the number of repaired roads in the Gatchina municipal district has decreased compared to previous years.
The total number of public road transport routes in the Gatchina municipal district has decreased, and the rolling stock of road transport in the municipal region and the city has also significantly decreased, which indicates a deterioration in the level of transport services for the population by road transport.
Positive factors include an increase of more than three times in the number of public suburban railway transport routes in the Gatchina municipal district.
The level of accessibility of transport infrastructure for people with disabilities and other groups of the population with limited mobility remains extremely low.
In general, despite the importance of the development of the housing and communal services sector, currently the most pressing issues of infrastructure development are being resolved at a rather slow pace. This is due to a number of reasons: the initially high degree of depreciation of fixed assets, the low level of provision of infrastructure facilities, especially in rural settlements, and the lack of an effective system of financing this area determined the main directions of development primarily through solving accumulated problems, rather than development.
The block of indicators for comparative analysis based on assessments for urban and rural settlements presents the following indicators:
Number of non-gasified settlements;
Characteristics of heating, water supply, sewerage and electricity networks according to the following indicators: total length of networks, the proportion of those in need of replacement and the proportion of those repaired in 2014 from those in need of replacement.
Table 29.
Comparative characteristics of indicators development of communal infrastructure for municipalities of the Gatchina municipal district
| Settlement | Number of non-gas-connected settlements | Heating system | Water supply system | Drainage system | Power supply system | |||||||||
| Length of heating and steam networks in two-pipe calculation, meters | Single length of street water supply network, meters | % of those in need of replacement of the total length | repaired as a percentage of those in need of replacement | Single length of street sewer network, meters | % of those in need of replacement of the total length | repaired as a percentage of those in need of replacement | Single length of street power line, meters | % of those in need of replacement of the total length | repaired as a percentage of those in need of replacement | |||||
| Susaninskoe | 88,6 | 14,0 | 50,2 | 0,5 | 54,1 | 2,9 | 17,9 | 20,0 | ||||||
| Siverskoye | 59,1 | 17,7 | 81,9 | 0,2 | 61,3 | 1,2 | 3,5 | 63,1 | ||||||
| Vyritskoe | 64,9 | 17,5 | 74,8 | 34,2 | - | 27,5 | 10,7 | |||||||
| Rozhdestvenskoye | 29,5 | 52,2 | 46,9 | 20,8 | 44,1 | 4,2 | ||||||||
| Taitskoe | 56,7 | 4,2 | 0,1 | 9,1 | 5,7 | |||||||||
| Syaskelevskoe | 27,6 | 80,9 | 0,4 | 65,4 | 36,1 | 4,6 | ||||||||
| Elizavetinskoe | 47,5 | 10,4 | 99,8 | 0,1 | 75,2 | 0,01 | 4,3 | 8,0 | ||||||
| Gatchina | 31,9 | 10,4 | 0,5 | 92,2 | 0,1 | 39,9 | 1,2 | |||||||
| Bolshekolpanskoye | 30,5 | 66,8 | 0,1 | 49,0 | 45,8 | 2,5 | ||||||||
| Novosvetskoe | 74,3 | 3,4 | 68,5 | 0,6 | 75,0 | 0,1 | 39,7 | 2,5 | ||||||
| Druzhnogorskoe | 8 940 | 69,9 | 5 753 | 81,7 | 0,02 | 6 618 | 55,9 | - | 35,4 | 11,6 | ||||
| Kommunarskoe | 97,0 | 1,9 | 79,0 | 79,7 | 0,5 | 685,1 | ||||||||
| Voyskovitskoe | 9 280 | 83,8 | 14 148 | 78,5 | 0,2 | 8 456 | 74,5 | 0,1 | 14 500 | 34,5 | 6,0 | |||
| Kobrinskoe | 84,3 | 7,5 | 94,3 | 0,3 | 61,3 | 0,2 | 43,3 | 4,3 | ||||||
| Verevskoe | 71,5 | 42,6 | 74,3 | 44,2 | ||||||||||
| Pudomyagskoe | 37,5 | 66,6 | 0,1 | 47,1 | ||||||||||
| Pudostskoe | 78,2 | 1,8 | 94,2 | 0,03 | 77,6 | 33,7 | 2,7 | |||||||
| TOTAL | 51,2 | 7,3 | 70,8 | 0,3 | 74,7 | 0,5 | 26,5 | 6,1 | ||||||
Environment
The environmental situation in the Gatchina municipal district, in particular, has remained moderately tense over the past few years.
The ecological state of the Gatchina municipal district is generally favorable with minor problematic issues. The main environmental problem is the increase in the level of man-made pollution associated with the use of outdated equipment and technologies by individual enterprises.
Ambient air pollution municipal district is characterized by average indicators for the region. In recent years, there has been an increase in emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere from stationary sources in the Gatchina region, which may be due to an increase in the number of enterprises, as well as the use of outdated equipment and technologies by individual enterprises in the region. The main sources of pollutants: poultry industry enterprises, other large enterprises, as well as motor vehicles. In addition, on the territory of the Gatchina municipal district there is an underground gas storage station, which accounts for a significant amount of methane emissions (almost 80% of total methane emissions in the Leningrad region).
The main indicators in air samples that do not meet sanitary standards are: dust content, concentration of sulfur and nitrogen dioxides, carbon monoxide.
Table 30.
Water quality of surface water bodies(the main rivers of the area) are classified as polluted. This is largely due to the fact that industrial and agricultural enterprises in the region discharge significant volumes of insufficiently treated wastewater. At the same time, the increased concentration of iron, manganese and partly heavy metals in river waters is natural and is associated with the fact that swamp waters participate in the feeding of rivers.
The main factors of groundwater pollution(water supply sources) are untreated wastewater from settlements and surface runoff. There is no unified storm drainage system and storm water treatment. Storm wastewater is collected only from the territory of multi-storey buildings in the city of Gatchina and discharged into the river. Izhora and R. Kolpanskaya without treatment - there are no treatment facilities at the storm water outlets.
The main sources of pollution are public utilities, industrial enterprises, agricultural facilities, untreated rain and melt water from undeveloped areas, and pollutants from the atmospheric air.
The quality of water in centralized water supply systems generally meets the requirements of SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 “Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems". In some settlements, there is an excess of iron content in the water - Vyritsa, Siversky, Pudomyagi, Bolshie Kolpany; it is necessary to purify water from underground sources at iron removal stations.
Generally agricultural soils in the municipal area they are slightly polluted and are safe for cultivating agricultural crops.
One of the main issues, the solution of which falls within the powers of municipalities, remains sanitary cleaning of the territory. In the summer, a significant contribution to the generation of municipal solid waste (MSW) is made by the seasonal population and recreational residents, which is reflected in the total volume of MSW generation.

Collection and disposal of waste in populated areas is carried out by licensed organizations using special vehicles. Removal is carried out to authorized landfills. There are 2 solid waste landfills on the territory of the municipal district: Novy Svet-Eko LLC with an area of 43 hectares and a capacity of 901,275.2 tons/year (Novosvetskoye rural settlement) and the Ecomonitoring landfill with a capacity of 25,500 tons/year (Siverskoye urban settlement). The New Svet-Eco landfill accepts a large share of St. Petersburg’s waste. The Ecomonitoring landfill was excluded from the GRRORO in 2014 due to the expiration of the license.
A licensed landfill located in the municipal area, which meets modern standards, accepts and fully copes with the volume of waste removed from populated areas of the municipal area.
The main problems of handling production and consumption waste in the region are:
Unauthorized dumps, which occur mainly in the summer season around gardening, gardening and summer cottages, as well as along roads and railways;
Lack of selective collection of consumer and industrial waste at the sites of its original generation.
Industrial waste from enterprises is transported under contracts to the St. Petersburg State Unitary Enterprise "Landfill "Krasny Bor", mercury-containing waste (burnt-out, waste fluorescent lamps, mercury-containing lamps) under contracts is sent to specialized organizations for disposal (LLC "Ecological enterprise "Mercury", CJSC "PEKOP" and etc.). Enterprises carry out temporary storage of this waste in specially equipped places, in accordance with the developed draft waste generation standards and limits on their disposal.
There is still a problem with the population placing most of the fluorescent lamps in solid waste collection areas.
Radiation situation in most of the municipal area it is characterized by low values of the exposure dose rate of gamma radiation and the content of radioactive elements. The gamma background level is determined by natural (soil contamination with natural radionuclides from underlying soil-forming rocks with increased natural radioactivity) and (slightly) man-made sources (abundance of radiation hazardous objects, the possibility of transboundary pollution and pollution during the transit of goods, unauthorized waste disposal, as a result of surface redistribution Chernobyl fallout, etc.). Within the boundaries of the Gatchina municipal district there are territories that have been subjected to radioactive contamination as a result of past radiation accidents and incidents. The extreme southwestern part of the municipal area fell into the “Chernobyl footprint” zone.
The northern part of the municipal area is potentially hazardous to radon. It is here that dictyonema shales, rocks with a uranium content higher than the background, come to the surface or are located in close proximity to the earth’s surface. Being within the development of zones of tectonic disturbances and other heterogeneities in the geological structure, radon emanations are significantly higher.
Being radioactive, the gas penetrates through cracks in the soil of the earth's rocks, and then into building structures. By breaking down into radionuclides, radon increases the risk of non-cancerous diseases of the upper respiratory tract and cardiovascular diseases and becomes a cause of cancer. Up to 70% of the radioactive exposure a person receives during his life comes from radon. Radon accumulates, first of all, in poorly ventilated rooms on the first floors of houses - basements, in underground passages. Considering the danger of its impact on the human body, it is necessary to conduct research and disinfection in areas where toxic gas accumulates.
In general, the following factors influence the environmental situation in the Gatchina municipal district:
§ The main sources of air pollution are road transport and industrial enterprises.
§ Water bodies are polluted by storm drains discharged without treatment, as well as insufficiently treated wastewater from municipal facilities, industrial enterprises, and agricultural facilities.
§ The bacteriological state of unprotected or insufficiently protected groundwater horizons is unfavorable. The most used Ordovician aquifer for drinking water supply is poorly protected from surface pollution. Monitoring of potential sources of pollution in sanitary protection zones of wells, prevention of filtration of contaminated water from the soil surface into aquifers, and systematic observations of the chemical and bacteriological state of groundwater are required.
§ Currently, in the Gatchina municipal district, the problem of recycling production and consumption waste has not been fully resolved. As a result of the lack of a separate collection system, valuable secondary raw materials, including wood residues, scrap metal, waste paper, etc., end up in the solid waste landfill.
§ The problem of the formation of unauthorized landfills and waste piles, which are sources of environmental pollution, remains.
§ The radiation background of the municipal area has been at a stable level over the past years.
§ The northern part of the municipal area is potentially hazardous for radon. It is necessary to carry out mandatory radon protection measures during new construction and their implementation, to the extent possible, in existing public and residential buildings within zones of increased radon concentration in soils.
Size: px
Start showing from the page:
Transcript
1 Development of housing and communal services and engineering infrastructure In order to develop housing infrastructure, the implementation of a short-term plan for the implementation of a regional program for the overhaul of apartment buildings has been organized. Over the first 9 months of 2016, major repairs were completed in 115 apartment buildings, and repairs are ongoing in 36 buildings. A short-term plan for the implementation of regional programs in years with a total volume of houses under renovation of 342 units was also approved. A new approach to the selection of contractors for major repairs has been implemented: based on the results of the competitive selection, a register of qualified contractors has been formed, which includes 17 organizations. Regional legislation on the issues of capital repairs of apartment buildings has been improved: the functions of a technical customer can now be transferred to local governments, the list of types of work on capital repairs has been supplemented with a technical inspection of common property in apartment buildings and an examination of design documentation. The period for the entry into force of the owners’ decision to terminate the formation of a capital repair fund for an apartment building on the account of a regional operator and its formation on a special account has also been reduced from 2 years to 1 year. The Irkutsk Region Law 65-OZ was adopted, according to which a measure of social support is provided for the payment of contributions for major repairs to citizens over 70 and 80 years of age (50% and 100%, respectively). As part of the implementation of measures to modernize the municipal infrastructure of the Irkutsk region, the development and approval of water supply and sanitation schemes in 178 and heat supply schemes in 176 municipalities of the Irkutsk region have been completed, and work is underway to update them in 2016. In 2016, subsidies were provided for the Irkutsk region from the federal budget within the framework of the Federal Target Program “Protection of Lake Baikal and Socio-Economic Development of the Baikal Natural Territory for the Years” of the state program of the Russian Federation “Environmental Protection” for the years: 1) in the amount of 702.9 million rubles for reconstruction sewerage treatment facilities on the right bank of the city of Irkutsk. The implementation of this activity is envisaged over the years with co-financing from extra-budgetary sources (funds from the Municipal Unitary Enterprise "Vodokanal" of the city of Irkutsk) in a total amount of 988.9 million rubles, including in 2016 - 113.5 million rubles. 2) in the amount of 145.1 million. rub. for the construction of a water heating line with two CH-750 boilers in the municipal district of Svirsk, st. Industrial site.
2 2 The Government of the Irkutsk Region pays special attention to attracting private investment into the utility sector of the economy of the Irkutsk Region for the purpose of construction, reconstruction, and modernization of utility infrastructure facilities. In 2016, local government bodies of municipalities in the region are preparing documentation for conducting a competitive selection for the right to conclude 21 concession agreements, including negotiations on concluding an initiative concession. The region's housing and communal services complex has ensured trouble-free passage of the heating season and preparation of communal infrastructure facilities for the heating season. Heat supply to populated areas is provided by municipal heat sources and 13 thermal power plants. The regional operational headquarters operates on a permanent basis. Uninterrupted heat supply to Baikalsk has been ensured. In 2016, it is planned to implement measures for the construction, reconstruction and modernization of water supply, water disposal and wastewater treatment facilities, including the development of design estimates, on the territory of 13 municipalities. In 2016, from the emergency technical reserve of the Irkutsk region for the prevention and elimination of emergency (pre-emergency) situations that arose at housing and communal services and the social sphere of the Irkutsk region, materials and equipment were allocated to 56 municipalities. In order to implement state policy in the field of housing policy and energy in the Irkutsk region since the beginning of 2016: - 113 agreements have been concluded on the provision of subsidies in order to compensate for lost income in connection with the provision of services in the field of electricity, gas, heat and water supply, sewerage and cleaning wastewater for a total amount of 90 thousand rubles, the regional budget provides for 100% of the subsidy required for 2016; - 36 agreements were concluded on the provision of subsidies at the expense of the regional budget for the purpose of financial support (reimbursement) of costs associated with the acquisition and delivery of fuel and energy resources for the provision of services in the field of electricity, heat and hot water supply in the amount of thousand rubles (95 % of annual volume); - subsidies were provided for the purchase, supply and storage of petroleum products necessary for power supply to settlements, as well as the maintenance and servicing of diesel power plants on the balance sheet of municipal institutions, financed in the amount of 4 thousand rubles (92% of the allocated allocations). 578 tons of diesel fuel were purchased and delivered to the settlements of Tofalaria; - subsidies have been provided for the purchase of diesel power plants, spare parts and materials for the repair of diesel power plants since the beginning of 2016, financed in the amount of thousand rubles (89% of
3 3 appropriations). Purchased and delivered to the village. Verkhnyaya Gutara diesel power plant. In order to develop gasification of the Irkutsk region: - an agreement was concluded to provide subsidies from the regional budget to the budget of the municipal formation of the city of Bratsk for the implementation of measures in the field of gasification and gas supply in the Irkutsk region in 2016 for a total amount of 3 thousand rubles. The agreement provides for the purchase of buses and housing and communal services equipment running on gas engine fuel in the amount of 3 thousand rubles, as well as subsidizing organizations for partial reimbursement of the costs of gasification of households, to which natural network gas is supplied, for all categories of citizens, living in the territory of the Irkutsk region, with the exception of preferential categories of citizens, in the amount of 2,000.0 thousand rubles. - to prepare for the reception of network gas from the Kovyktinskoye gas condensate field (OJSC Gazprom) of consumers in the village of Zhigalovo, 5.5 km of intra-village gas distribution networks were built for a total amount of 13.4 million rubles, including at the expense of the federal budget - 7.4 million . rubles, at the expense of the regional budget 6.0 million rubles. In accordance with the subprogram “Energy saving and increasing energy efficiency in the Irkutsk region” for the years of the state program “Development of housing and communal services in the Irkutsk region” for the years, approved by Decree of the Government of the Irkutsk region dated October 24, 2013 446-pp, lists of projects in the region were approved energy saving and increasing energy efficiency, implemented in the Irkutsk region in 2016: In the direction of major repairs of electrical grid facilities, major repairs of a power line - 0.4 kV in the Oktyabrsky-Maninsk settlement in the Usolsky district of the Irkutsk region (Razdolinsky municipal formation of the Usolsky district of the Irkutsk region, for the amount of co-financing 5,500.0 thousand rubles); In the direction of registration and registration of municipal ownership rights to ownerless electric grid facilities (Veselovskoye municipal formation of the Chunsky district, Kazachinsko-Lensky municipal district, Kirensky municipal district, municipal formation "Kutulik" of the Alarsky district, Taitursky municipal formation, for the amount of co-financing 553.0 thousand rubles). Competitive procedures are being carried out to determine the contractor to carry out work on the preparation of the Fuel and Energy
4 4 balance sheet of the Irkutsk region and the development of a Scheme and program for the development of the electric power industry of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation. By Order of the Governor of the Irkutsk Region No. 135-r dated October 17, 2016, a list of consumers of electrical energy (power) was approved, limiting the mode of consumption of electrical energy for which can lead to economic, environmental and social consequences. Transport Main results in the development of the region's transport system based on the results of 9 months of 2016: 1. As of October 1, 2016, people were transported along subsidized inland water transport routes, which is 902 people less than in the same period in 2015. The decrease in the number of passengers transported over 9 months of 2016 was due to the termination of subsidies for the Osetrovo Alekseevsk Osetrovo route in 2016 due to the lack of carriers. In 2017, it is planned to restore subsidies for this route. Since June 1, 2016, on the territory of the Irkutsk region there have been 2 specialized parking lots for detained small vessels on the territory of the Irkutsk Reservoir (Captains Club LLC on the territory of the Irkut Yacht Club) and the Bratsk Reservoir (Avtolight LLC). During the period of operation of the moorings, 14 small vessels were detained, of which 11 were in the Irkutsk Reservoir and 3 in the Bratsk Reservoir. It is planned to open a specialized parking lot for small vessels in the city of Ust-Kut. 2. For 9 months of 2016, passengers were transported by rail in total: thousand people (101.8% compared to the same period in 2015). A perpetual license was received from OJSC “Baikalskaya PPK” to carry out activities for the transportation of passengers by rail in suburban traffic dated March 25, 2016 (PP series) with the places of implementation of the licensed type of activity: Trans-Baikal Territory, the Republic of Buryatia, Irkutsk Region, Krasnoyarsk Territory. A comprehensive transport service plan for the medium and long term (CPTO) has been developed and approved. 3. As of October 1, 2016, the register of intermunicipal routes for regular transportation of passengers and luggage by road in the Irkutsk region includes 280 routes. Over the first 9 months of 2016, the Ministry reviewed 729 applications for permits to carry out activities for the transportation of passengers and luggage by taxi in the Irkutsk region. According to the results
5 5 consideration of applications, 1976 permits were issued, and refusals to issue permits were issued in relation to 169 vehicles. 4. For 9 months of 2016, a person was transported along subsidized air transport routes by local airlines; for the same period in 2015, a person was transported. The decrease in the number of passengers carried over the 9 months of 2016 was due to the termination of subsidies for the Irkutsk Bratsk Irkutsk route in 2016 and the termination of passenger transportation by PANH Aviation Company LLC in May 2016. For 9 months of 2016, as part of the provision of subsidies to the municipal formation of Nizhneudinsky district to compensate for the costs of transporting passengers and cargo necessary for the life support of the population, 4,444 people were transported by air; during the same period in 2015, 3,052 people were transported. Deputy Minister A.A. Trifonov
Ministry of Housing Policy, Energy and Transport of the Irkutsk Region BRIEF REPORT ON THE WORK DONE FOR THE 1st QUARTER OF 2016 Main results of activities. Development of communal infrastructure:
Communal infrastructure: Repair and reconstruction of communal infrastructure: 24 block-modular heat sources were built; 50 heat sources were reconstructed and repaired; 123 km of thermal, water,
Explanatory note to the report Subprogram 1 “Development of housing and communal services in the Sverdlovsk region” for the first quarter of 2015. 1) Information on the implementation of state program activities,
Ministry of Housing Policy and Energy of the Irkutsk Region in figures and facts Housing and communal services are one of the priority and key areas of development of the territories of the Irkutsk region,
GOVERNMENT OF THE IVANOV REGION DECISION dated December 15, 2014 532-p Ivanovo On the provision of subsidies to the budgets of municipalities of the Ivanovo region for the organization of water supply and
Appendix to the resolution of the Government of the Murmansk region from the “LONG-TERM TARGET PROGRAM “Comprehensive development of public utility infrastructure systems in the Murmansk region” for 2011-2015 Murmansk 2011
GOVERNMENT OF THE IVANOV REGION DECREE dated 10/07/2014 412-p Ivanovo On the provision of subsidies to the budgets of municipalities of the Ivanovo region for the organization of heat supply to consumers
DECISION of the administration of the municipal formation "Makarovsky urban district" of the Sakhalin region dated June 28, 2018 488 Makarov On amendments to the municipal program "Providing for the population
CP “Centralized power supply to settlements of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug of Ugra for 2011-2013 and for the future until 2015” On the territory of Ugra in the zone of decentralized power supply
03.29.2018 562 On introducing changes and additions to the municipal program “Implementation of the main directions of the construction complex, housing and communal services, road services, improvement, transport
GOVERNMENT OF THE NOVOSIBIRSK REGION DECISION dated May 24, 2010 16-p On approval of the Conditions for the provision and expenditure of subsidies to local budgets to support capital projects
APPENDIX 5 to the decision of the Council of Deputies of the city of Kirovsk from the Distribution of budget allocations by sections, m, target items and types of expenses of the classification of budget expenses for 2012 type (thousand rubles)
SUBPROGRAM "Modernization of municipal infrastructure facilities" of the regional long-term target program "Stimulating the development of housing construction in the Bryansk region in 2011-2015" Passport
Abstracts of the speech by V.N. Silkin, Chairman of the Ivanovo Region Committee on Transport at a meeting of the Government of the Ivanovo Region on November 12, 2013 Dear Pavel Alekseevich! Dear members of the Government
ADMINISTRATION OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION “PRIMORSKY URBAN SETTLEMENT” VYBORG DISTRICT OF THE LENINGRAD REGION DECISION of March 05, 2019 226 “On amendments to the Administration Resolution
REPORT ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PUBLIC DECLARATION of priority goals and objectives of the Ministry of Energy and Economy for 2016 Key goals Program priority tasks Report on the implementation for 2016 S/P activities
ADMINISTRATION OF SURAVSKY VILLAGE COUNCIL OF TAMBOV DISTRICT OF TAMBOV REGION RESOLUTION _04/01/2016_ village surava 26 On approval of the target program “Comprehensive program for the development and modernization of facilities
Approved by: decision of the Council of Deputies of the municipal formation Gromovskoye rural settlement of the Priozersk municipal district of the Leningrad region dated November 25, 44 Appendix 7 Departmental structure
APPROVED by the Decree of the Government of the Altai Republic of 2012 REPUBLICAN ADDRESS PROGRAM “Major repairs of apartment buildings in the Altai Republic in 2012” I. Passport
December 21, 2015 160-OZ LAW OF THE SVERDLOVSK REGION ON THE ORGANIZATION OF TRANSPORT SERVICES FOR THE POPULATION IN THE TERRITORY OF THE SVERDLOVSK REGION Adopted by the Legislative Assembly of the Sverdlovsk Region on December 15
DECISION of the administration of the municipality of the Sakhalin region dated March 21, 2017 285 Makarov On amendments to the municipal program “Providing for the population of the municipality
GOVERNMENT OF THE IVANOVSK REGION DECREE dated December 06, 2017 458-p Ivanovo On approval of the state program of the Ivanovo region “Providing housing and communal services to the population
Art. 1552 262 7 1552 DECISION OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF KARELIA On amendments to Government Decree of June 20, 2014 197-P The Government decides: To include in the state program
Deputy Chairman of the Committee on Energy and Engineering Support Committee on Energy and Engineering Support 190000, St. Petersburg, per. Antonenko, 4 Qualification requirements Work experience
“x o d. 1 * 1 * C” -Yu. 20"/ MINUTES SIGNATURE of the meeting of the working group for the selection of municipalities of the Irkutsk region to provide subsidies from the regional budget to local budgets for development
APPROVED by Head of the Leningrad Region Transport Department P.M. Postovalov 2017 REGULATIONS on the transportation organization department of the Leningrad region transport department 1. General provisions 1.1.
REPORT on the implementation of the program “Development of housing and communal services and increasing energy efficiency in the region until 2020” Form 1 line Goals, objectives and targets Achievement of targets
Approved by resolution of the administration of the North-Evensky district dated October 1, 214 243-pa (as amended by resolutions dated December 22, 214 322-pa, 26.2.215 57-pa, 22.6.216 298-pa, 1.8.216 37-pa, 12.1 .216 438-pa,
GOVERNMENT OF THE ORENBURG REGION REGULATION 12/29/2016 Orenburg 1008-pp On amendments to the Government Resolution dated 08/30/2013 739-pp 1. Introduce into the Government Resolution
Appendix to the resolution of the administration of the city of Murmansk dated July 30, 2013 1968 Departmental target program “Preparation of housing and communal services facilities of the municipal formation of the city of Murmansk
GOVERNMENT OF THE ORENBURG REGION REGULATION 03/31/2014 Orenburg 185-p On approval of evaluation criteria for selecting construction projects, modernization and major repairs of facilities
GOVERNMENT OF THE MOSCOW REGION DECISION N 349/16 of May 16, 2014 ON APPROVAL OF THE PROCEDURE AND CONDITIONS FOR PROVIDING STATE SUPPORT FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE REGIONAL CAPITAL REPAIR PROGRAM
MINISTRY OF Housing and Communal Services of the Rostov Region ORDER October 12, 2012 123/1 Rostov-on-Don On amendments to the order dated January 12, 2012 8 In order to implement the Regional Long-Term
ADMINISTRATION OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION CITY SETTLEMENT OF PECHENGA PECHENGA DISTRICT OF THE MURMANSK REGION DECISION of June 27, 2018 122 p. Pechenga On amendments to the municipal program
Municipal formation "City of Birobidzhan" of the Jewish Autonomous Region CITY CITY HALL DECREE 02/13/2018 354 Birobidzhan On amendments to the city mayor's resolution of 12/07/2016 3637 "On
Conclusion based on the results of the financial and economic examination of the draft resolution of the Government of the Krasnoyarsk Territory “On amendments to the resolution of the Government of the Krasnoyarsk Territory of September 30, 2013
“Appendix 2 to the resolution of the Administration of the Odintsovo municipal district dated 08/08/2017 4422 3. METHODOLOGY FOR CALCULATING THE VALUES OF EFFICIENCY INDICATORS FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE MUNICIPAL PROGRAM Efficiency
DECISION OF THE COUNCIL OF DEPUTIES OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION ORYOL VILLAGE COUNCIL OF THE KIROV DISTRICT OF THE STAVROPOL TERRITORY December 22, 2015 With. Orlovka 26 About the target program of the municipal formation Orlovsky
BUDGET FOR CITIZENS PART 6 STATE PROGRAMS DIRECTED TO ACHIEVE THE GOAL “Balanced territorial development through infrastructure development in the Tomsk region” INTRODUCTION 2 Presented
Information on the work of the Housing and Communal Services Department of the Administration of the Municipal Municipality "Sarapulsky District" for 2015 Program: Maintenance and development of communal infrastructure A KV0.63Gs boiler was installed in the boiler room
Regional seminar-meeting “Tariff regulation 2017 and the tasks of the Tariff Regulation Committee of the Murmansk region for the next regulation period” March 24, 2017 Murmansk Introduction
GOVERNMENT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION DECISION N 1225 of December 31, 2009 ON REQUIREMENTS FOR REGIONAL AND MUNICIPAL PROGRAMS IN THE FIELD OF ENERGY SAVING AND INCREASING ENERGY EFFICIENCY
PSKOV REGIONAL ASSEMBLY OF DEPUTIES RESOLUTION on the Law of the Pskov Region “On the participation of the Pskov region in public-private partnerships” The Regional Assembly of Deputies DECIDED: 1. Adopt
Administration of the Nikolaevsky district MUNICIPAL PROGRAM “Development of passenger transport and transport infrastructure in the Nikolaevsky municipal region” Responsible executor: Reporting year:
RUSSIAN FEDERATION VLADIMIR REGION LAW On the organization of transport services for the population in the Vladimir region Adopted by the Legislative Assembly of the region on April 25, 2018 Article
ADMINISTRATION OF THE PERM MUNICIPAL DISTRICT DECISION On amending the appendix of the resolution of the administration of the Perm Municipal District dated 06/02/2014 2192 In accordance with Art. 51-6.
ADMINISTRATION OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION “Kamennogorsk urban settlement” of the Vyborg district of the Leningrad region DECISION of April 9, 2019 124 On amendments to the administration resolution
ADMINISTRATION OF THE RURAL SETTLEMENT OF SVETLY, Berezovsky district of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug-Ugra DECISION dated 01/13/2014 4 p. Svetly On approval “Development of the housing and communal services complex
GOVERNMENT OF THE TULA REGION DECISION Fri 02/20/2018 j\b 69 On introducing amendments and additions to the resolution of the government of the Tula region dated 11/19/2013 660 In accordance with Article 48 of the Charter
ADMINISTRATION OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION “Kamennogorsk urban settlement” of the Vyborg district of the Leningrad region DECISION of February 25, 2019 74 On amendments to the administration resolution
Subprogram “Energy saving and increasing energy efficiency on the territory of the Komi Republic” Deputy Head of the Komi Republic Tariff Service Pavel Petrovich Secretaryev Regional
ADMINISTRATION OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION OF THE CITY DISTRICT "OKHINSKY" DECISION dated 08/14/2017 800 On amendments to the resolution of the administration of the municipal formation "OKHINSKY" dated 12/23/2013
RUSSIAN FEDERATION IRKUTSK REGION BRATSKOY DISTRICT VIKHOREVSKY MUNICIPAL FORMATION ADMINISTRATION DECISION of 08.10.2018 184 Vikhorevka ON CHANGES TO THE MUNICIPAL PROGRAM OF VIKHOREVSKY
DATA on the progress and results of implementing measures to save energy and improve energy efficiency in the housing stock of the Kirov region as of 01/01/2017 To meet the requirements
Order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Energy of Russia) dated October 13, 2014 N 721 Moscow “On approval of the Rules for the provision of subsidies from the federal budget to legal entities for
APPROVED by Decree of the Government of the Irkutsk Region dated March 20, 2014 138-pp. REGIONAL PROGRAM FOR CAPITAL REPAIRS OF COMMON PROPERTY IN APARTMENT BUILDINGS IN THE TERRITORY OF THE IRKUTSK REGION
MEETING OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE MURMANSK REGION May 3, 2018 Murmansk Report on the results of the activities of the Ministry of Transport and Road Facilities of the Murmansk Region in 2017 Minister of Transport and
Appendix 12 to the draft district budget for 2015 and for the planning period 2016 and 2017" Subsidies to legal entities (except for subsidies to municipal institutions), individual entrepreneurs,
RUSSIAN FEDERATION IRKUTSK REGION MUNICIPAL FORMATION “UST-KUT CITY” ADMINISTRATION DECISION dated 12/26/2016. 2822-p On approval of the Regulations on the provision of subsidies from the municipal budget
Request to change the passport of the priority regional project “Ensuring the quality of housing and communal services in the Sverdlovsk region” 1. General information on the request for change Date of the request for change
Expenditures and target indicators of the state program of the Perm Territory “Development of the transport system” for the period 2017 and the planning period of 2018 and 2019 Speaker: Zakiev Almaz Rashitovich, Minister of Transport
ADMINISTRATION OF THE MUNICIPAL FORMATION CITY SETTLEMENT OF PECHENGA PECHENGA DISTRICT OF THE MURMANSK REGION DECREE dated November 19, 2018 230 Pechenga settlement On approval of the municipal program “Development”
“On the state and prospects for the development of heat supply systems located on the territory of municipalities of the Sverdlovsk region” Acting. Minister of Energy and Housing and Communal Services of Sverdlovsk
GOVERNMENT OF THE KURGAN REGION RESOLUTION of April 21 N 152 ON THE APPROVAL OF THE PLAN FOR REFORMING THE HOUSING AND COMMUNAL SECTOR OF THE KURGAN REGION FOR THE PERIOD UNTIL 2011 (as amended by the Resolution of the Kurgan Region
December 27, 2007 N 1001 OZ LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY OF THE OMSK REGION LAW OF THE OMSK REGION ON THE TARGET PROGRAM OF THE OMSK REGION "DEVELOPMENT OF THE HOUSING AND UTILITIES COMPLEX OF THE OMSK REGION" FOR 2008 2010
On the organization of major repairs of common property in apartment buildings in the Tyumen region Regional program for major repairs of common property in apartment buildings in the Tyumen region 7,249 apartment buildings
July 5, 2013 N 360-OZ NOVOSIBIRSK REGION LAW ON THE ORGANIZATION OF CAPITAL REPAIRS OF COMMON PROPERTY IN APARTMENT BUILDINGS LOCATED IN THE TERRITORY OF THE NOVOSIBIRSK REGION Adopted by resolution
Approved by the Resolution of the district administration dated December 1, 2010 955 Municipal target program “Providing the population of the district with drinking water for 2011-2013” p. Rzhaksa village 2010 Program Passport
Limited Liability Company "Project Service" Certificate of admission to work on the preparation of project documentation dated January 10, 2013. P.037.76.4477.01.2013 Materials to justify the changes
EXPLANATORY NOTE “On the status of consideration of citizens’ appeals and the organization of personal reception in local government bodies of the Lyubinsky municipal district for 2011.” Review status analysis
The development of the republic's housing and communal services in 2008-2012 will be aimed at increasing the efficiency, sustainability and reliability of the functioning of housing and communal life support systems, improving the quality of maintenance and repair of the housing stock, providing housing and communal services to the population while simultaneously reducing irrational costs.
In this regard, the following tasks must be solved:
Reorganization of property, financial and contractual relations in the housing and communal services sector, attracting private business to manage residential buildings and communal infrastructure, ensuring an influx of private investment into the industry;
Transition to payment for housing and communal services by the population in accordance with federal standards, ensuring social protection of the population when paying for services, defining standards for cost, payback and maximum permissible expenses of citizens at the level of ulus entities;
Creation of conditions for the formation and activities of homeowners’ associations;
Organization of work with the population to create homeowners' associations;
Reducing the cost of housing and communal services through the use of energy-saving technologies and the formation of a market economic system.
Main directions of industry development:
Renewal, modernization and technical re-equipment of fixed assets;
Solving issues of drainage and water supply to populated areas;
Introduction of new energy and resource saving technologies;
Introduction of effective forms of economic relationships;
Improving the quality of provision of housing and communal services;
Development of mechanisms for attracting investments for the modernization and technical re-equipment of housing and communal services facilities;
Holding competitions by heads of municipalities for housing maintenance among management companies.
Preservation of public utility property in state ownership in order to develop processes for concluding concession agreements with operating organizations on a competitive basis.
The process of introducing contractual relations between the “customer and the contractor”, in the uluses and cities of the republic, “Management company - supplier of housing and communal services” is being completed. In 2008, the privatization of the State Unitary Enterprise Housing and Communal Services of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) and the State Unitary Enterprise Vodokanal will be carried out through the creation of joint-stock companies. In 2009, the liquidation of all non-operating enterprises in the industry will be completed. The task has been set - by 2010, to create a unified information system for the database of consumers of housing and communal services - to introduce the “Single Window” principle throughout the republic.
As part of the modernization of municipal boiler houses, it is envisaged to transfer boiler houses to gas fuel, transfer boiler houses from gas condensate and oil boiler fuel to coal, reconstruction and construction of boiler houses. In water supply and sanitation, reconstruction and construction of water intakes with water treatment facilities, reconstruction and construction of centralized wastewater disposal systems will be carried out.
In the gasified regions of the republic, it is planned to convert 100 boiler houses (out of 120) to gas, which will allow annual savings of 120.9 million rubles at the end of the implementation of the measures. Of the 318 boiler houses operating on liquid fuel, 116 boiler houses will be converted to coal, the economic effect will be 555.1 million rubles per year, 11.9 thousand tons of gas condensate boiler fuel and 86.4 thousand tons of oil boiler fuel will be replaced.
It is planned to build and reconstruct 12 water intakes with a water purification complex, 2 sewerage treatment facilities. In order to modernize the fleet of specialized municipal equipment, it is planned to purchase 207 units of equipment.
Measures are provided aimed at stimulating the energy saving process and creating the necessary conditions for the introduction of energy saving technologies.
In order to unify approaches and simplify procedures for approving tariffs for housing services by the population, it is planned to develop a recommendatory price list of tariffs for housing services.
Tariff policy in the housing and communal services sector will be aimed at gradually increasing the share of payments for housing and communal services by the population, subject to preventing a sharp increase in the burden on household budgets. Taking this into account, the return on utilities for the population in the coming five years in cities can be increased to 75-85%, in rural areas - up to 35%.
Solving the problems of modernizing the utility complex requires the development of comprehensive programs for the development of utility infrastructure at the level of each municipality on the basis of master plans for the development of settlements in accordance with the requirements of the Federal Law of December 30, 2004 No. 210-FZ “On the basis for regulating tariffs of organizations of the utility complex.”
In order to increase the efficiency and quality of housing and communal services to the population, the State Program “Reform and development of the housing and communal complex of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) for 2007-2011” was developed.
The implementation of the Program is closely related to the implementation of the following programs:
Federal target program “Housing” for 2002-2010. subprogram “Modernization of municipal infrastructure facilities”,
Federal target program “Economic and social development of the Far East and Transbaikalia for 1996-2005 and until 2010”,
State program “Gasification of settlements of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) in 2007-2011 and the main directions of gasification until 2020” subprogram “Conversion of boiler houses to gas fuel”,
Republican target program “Housing” for 2006-2010, subprogram “Modernization of utility infrastructure facilities”,
State program “Environmental protection of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) for 2007-2011.”
6.3.1. Characteristics of the housing and communal complex
GO "City of Yakutsk"
The housing and communal services sector of the City of Yakutsk remains characterized by the low efficiency of the existing industry management system with many unresolved problems. Today, such conclusions are based on the following negative trends. So, in the city of Yakutsk:
Enterprises in the housing and communal services sector remain unprofitable;
A fundamental problem remains the significant deterioration of the housing stock, leading to an increase in accidents and the provision of poor-quality services;
Private initiative and competition, market relations in the housing and communal services sector are insufficiently developed, there is no targeted work in the media to form the self-awareness of the city dweller as the owner of his city in order to prevent damage to city property, ensure cleanliness and sanitary well-being;
There are no mechanisms for attracting investment in the development of housing and communal services;
The construction of new housing stock on the territory of the urban district is being carried out poorly with a lot of deficiencies, which entails obvious problems in the operation of the housing stock;
The current system of maintenance and repair of the housing stock does not ensure proper maintenance of housing, there is significant underfunding, and the quality of the work performed does not fully meet the requirements. There is a need to carry out a wider range of measures to organize repair and construction work and search for real sources of financing for capital and current repairs of the housing stock;
There is low efficiency of energy systems and significant losses of resources, and there are interruptions in the supply of heat, water and electricity to consumers. Losses of energy and water resources dictate the need to develop a targeted policy of energy and resource conservation, first of all, to organize the accounting of heat and water consumption;
The technical condition of intra-block territories in most districts of the municipality "Yakutsk" requires intensifying the improvement policy by attracting significant resources and their effective use;
There is a gradual swamping of the territory and a deterioration in the sanitary condition of the city as a whole and its individual districts, requiring comprehensive measures for drainage, cleaning and sanitary cleaning of the city territory, focused on the separate collection of household waste, competitive distribution of orders for carrying out relevant work;
Providing the population with green spaces does not meet the standard level, as a result of which there is a growing need for the development of gardening and park management of the GO “Yakutsk City” with additional attraction of financial resources and competent organization of the management system for this complex;
Insufficient attention to certain aspects of housing and communal services, bordering on social ones;
Dependence of producers of housing and communal services on budget subsidies, a significant amount of underfunding of the industry,
High degree of depreciation of fixed assets of housing and communal services enterprises,
The actual lack of opportunity for service recipients to influence their quantity and quality,
High costs and lack of economic incentives to reduce costs, ineffective and unprofitable work of housing and communal services enterprises, high level of resource losses.
All this is, on the one hand, a consequence of the inertia of the processes occurring in the industry, and on the other hand, the result of the lack of a mechanism for solving problems within the framework of the current municipal target program “Reform and development of housing and communal services of the Municipal Municipality “Yakutsk City” for the period 2004-2010 years." This Program does not provide for measures to introduce new forms of economic relationships in the housing and communal services sector, measures for the financial rehabilitation of housing and communal services enterprises, measures for inventory of assets and revaluation of fixed assets; the mechanism and sequence of structural transformations in the housing and communal services industry, personnel management in the housing and communal services industry, principles and procedures for the transfer of property are not reflected. A mechanism for attracting investments in the housing and communal services sector on co-financing terms has not been developed.
Due to the presence of a large number of unsolved problems in the housing and communal services of the municipality "Yakutsk", the low efficiency of the current municipal target program "Reform and development of housing and communal services of the municipal municipality "Yakutsk city" for the period 2004 - 2010." for 2008, a new Municipal target program was developed for the integrated development of the housing and communal complex of the municipality "Yakutsk" for the period 2007-2013 and the main directions until 2020.
6.3.2. System of program events
for the development of housing and communal services of the State Municipality "City of Yakutsk"
The system of program measures for the development and reform of the housing and communal complex of the municipality "Yakutsk" will be carried out within the framework of the Municipal target program "Comprehensive development of the housing and communal complex of the municipality "Yakutsk" for the period 2007 - 2013 and the main directions until 2020", Federal Law-185 “On the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services”, the republican target program “Housing” for 2006 - 2009”, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) dated 12/14/06. No. 656
In pursuance of Federal Law-185 “On the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services” dated July 21, 2007. approved republican targeted programs “Resettlement of citizens from emergency housing stock for 2008”, approved by Order of the President of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) No. 196 dated April 30, 2008, and “Major renovation of apartment buildings in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) for 2008”, approved by Order of the President RS (Y) No. 202-RP dated May 13, 2008.
According to the program “Major repairs of apartment buildings in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) for 2008,” it is planned to carry out major repairs of multi-apartment housing stock in the amount of 61 buildings with a total housing area of 209.921 thousand square meters. meters.
During the development of the targeted program of the GO "Yakutsk" for the overhaul of apartment buildings, an action plan was approved for the implementation of the Federal Law of July 21, 2007 No. 185-FZ (hereinafter - Federal Law No. 185), a commission was created for the implementation of Federal Law No. 185 and a commission for working with population to create homeowners' associations (hereinafter - HOA);
Events held:
1. A draft of the Municipal Targeted Program “Major repairs of apartment buildings in the Yakutsk Urban District” has been developed as part of the implementation of the Federal Law of July 21, 2007 No. 185-FZ “On the Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services” for 2008.”
2. In the period from February 19 to February 23, 2008, on behalf of the Chairman of the Government of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) E.A. Borisov, members of the commission of the GO "Yakutsk" as part of the republican delegation to the Ministry of Housing and Communal Services and ERS (Yakutia) were sent to Moscow, to the State Corporation - Fund for Assistance to the Reform of Housing and Communal Services (hereinafter - FSR Housing and Communal Services) to study the issue of forming an application for financial support from the Fund .
During the development of the targeted program of the Municipality "Yakutsk" for the resettlement of citizens from emergency housing stock, the following activities were carried out:
1. Meetings of homeowners of emergency apartment buildings were held at the following addresses: Dzerzhinsky, 49,51,57,59, Kuzmina, 30/2. Based on the results of the meetings, decisions were made to participate in the PC (Y) targeted program for the relocation of citizens from dilapidated housing.
2. A list of apartment buildings has been prepared for which it is planned to provide financial support for the resettlement of citizens within the framework of the PC (Y) targeted program.
The district administration has developed a plan of priority measures to resolve a set of issues regarding the creation of homeowners' associations (HOAs) in stone apartment buildings (MADs) on the territory of the GO "Yakutsk City" in accordance with Government Resolution No. 185 of May 14, 2008 "On the formation of Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) favorable conditions for the formation and activities of homeowners’ associations.” It includes the following activities:
Creation of a center for assistance to homeowners' associations under the District Administration of the City of Yakutsk;
Organization and creation of HOAs on the territory of the municipality "City of Yakutsk"
Working with the media on coverage. Advantages of HOA;
Advanced training for managers and specialists of HOAs and management companies;
Rule-making activities on the activities of HOAs;
The immediate tasks for including and promoting the application of the GO “City of Yakutsk” to receive financial support from the Housing and Communal Services Reform Assistance Fund are the following:
1. Bringing the number of apartment buildings (hereinafter - MKD) in which HOAs have been created to the required volume of at least 5% of the total number (32 MKD).
2. Conducting general meetings of HOA members or owners of premises in apartment buildings to participate in the program and co-finance at least 5% of the cost of major repairs.
3. Obtaining a standard for the maximum cost of major repairs per 1 sq. m. area.
4. Formation of an address list of apartment buildings based on the calculation of the standard maximum cost of 1 sq.m. ;
5. Development of drafts of the required regulatory legal acts,
6. Formation of an application under the terms of Federal Law No. 185-FZ.
Table 6.3.2.1.
Distribution of financial support funds under the program “Major repairs of apartment buildings in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) for 2008” for the municipality “City of Yakutsk”
Solving problems associated with the reform and development of the housing and communal complex of the Urban District "Yakutsk City" until 2012 provides for a system of the following measures:
The system of program activities provides for the following measures:
1. Optimization of the management structure of the housing and communal services complex,
2. Creation of homeowners' associations (HOAs);
3. Increasing the role of territorial public self-government in urban management;
4. Financial recovery of industry enterprises;
5. Improving the personnel management system;
6. Creation of a competitive environment and the introduction of new forms of economic relationships in the field of housing and communal services;
7. Formation of favorable conditions for attracting investments in the housing and communal services complex;
8. Systematization and automation of accounting of technological processes, financial and economic activities and document flow of the housing and communal services complex;
9. Targeted program for major repairs of multi-apartment residential buildings;
10. Targeted program for the resettlement of citizens from dilapidated and dilapidated housing stock;
11. Modernization and technical re-equipment of housing and communal services;
12. Energy and resource conservation in the housing and communal services complex;
13. Solving the problem of draining neighborhoods of the city of Yakutsk and ensuring the flow of the city canal;
In order to increase the role of territorial public self-government in urban management, TOSs were created. On their basis, administrative districts (governments) were created, which are structural divisions of the District Administration of the city of Yakutsk. The councils exercise certain powers of local self-government in the respective territory. The main functions of the boards are:
Work on collecting information necessary for accounting of taxable objects in the territory of the municipality "Yakutsk City";
Control over the use of land plots and the construction of facilities on the territory of the council in accordance with the urban development plan for the territory;
Monitoring the proper maintenance, use, repair and operation of the housing stock, external systems of engineering equipment, adjacent areas with landscaping and landscaping facilities located on them, sanitary cleaning of households in compliance with current standards of technical operation and routine repairs on the territory of the Administration. Coordination and control of the activities of management companies and homeowners' associations regarding the quality of provision of housing and communal services;
Organization of work on intra-block improvement;
Organization and implementation of supervision and control of the implementation of mandatory legislative requirements in the field of ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population and in the field of environmental protection. Coordinate with supervisory authorities in the field of ensuring sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population and in the field of environmental protection;
Ensuring the protection of public order in the subordinate territory through interaction, control and organization of the activities of the relevant public order bodies (precinct, voluntary people's squad, police, etc.)
Diagram 6.3.2.1.
Expected results from implementation:
Improving the efficiency and quality of housing and communal services for the population;
Financial recovery of enterprises of the housing and communal services complex of the Urban District "Yakutsk City";
Ensuring stable and highly reliable operation of life support systems;
Creation of an effective economic mechanism for stimulating resource conservation.
Diagram 6.3.4.2.

Table 6.3.4.1
Forecast of the main indicators of housing and communal services of the State Municipality "City of Yakutsk" until 2012
| Index | Unit change | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
| Actual level of payment by the population for housing and communal services | % | 70,7 | 70,4 | 70,1 | ||||
| Total area of housing stock | Thousand sq. m. | 4569,8 | 4719,5 | 4873,3 | 5026,0 | 5178,8 | 5331,5 | |
| Central heating | % | |||||||
| Domestic water supply | % | |||||||
| Domestic drainage | % | |||||||
| Hot water supply | % | |||||||
| Number of families receiving subsidies for housing and utilities | units | 7 413 | 7 214 | 7 465 | 7 491 | 7 517 | 7 543 | 7 569 |
6.3.3. Water supply and sanitation
Providing the population with good-quality water that meets the requirements of sanitary rules and standards “Drinking water” is currently an urgent problem in the city of Yakutsk.
The source of water supply for Yakutsk is the Lena River. The water supply system includes a water intake with a capacity of 60 thousand cubic meters. m/day with a heating, disinfection complex and water storage tanks for 4000 cubic meters. The rise of water from the Lena River in 2006 amounted to 27.9 million cubic meters, water sales - 21.7 million cubic meters.
The city's need for drinking water is 90 thousand cubic meters. m/day. The water consumption deficit is compensated by a floating pumping station, however, this option provides the necessary water consumption only in winter. To ensure further development of the city, the capacity of water intake structures must be increased to 100 thousand m7day. Currently, the Yakutagropromproekt Institute has developed design documentation and is constructing a water intake and water treatment facilities with a capacity of 100 thousand m 3 /day.
The water intake structures include: a pumping station of the 1st lift (ditch) with a capacity of 60 thousand m 3 /day, a pumping station of the 2nd lift with a capacity of 60 thousand m 3 /day. 100 thousand m 3 /day, two clean water tanks (RCW) with a volume of 2000 m 3 each,
chlorination (for water disinfection).
Taking into account the growth rate of housing construction in Yakutsk, as well as due to the insufficient productivity of existing waterworks, it is necessary to construct waterworks No. 4 and reconstruct waterworks No. 6 with an increase in the capacity of each to 50 thousand cubic meters. m/day.
The city's water main networks, 108.4 km long, range in age from 1 to 27 years, about 50% are subject to replacement due to physical wear and tear and insufficient capacity.
Increasing the water supply to the city will require reliable, trouble-free operation of networks and sewerage facilities. Coverage of the population of Yakutsk by a centralized sewerage system is 75%. Sewage from residential buildings and other buildings flows through gravity sewers to sewage pumping stations, then is pumped through pressure pipelines to biological wastewater treatment plants (BWTP).
Sewer collector No. 1 passing through the streets: Lenin Ave., st. Dzerzhinsky, F. Popov St. with a diameter of 700 mm, laid in a passage tunnel, has been in operation since 1969, passes up to 24 thousand m 3 of wastewater per day and is in disrepair. To receive wastewater from the sewerage system, it is necessary to build a drainage station with a capacity of 15 thousand cubic meters. m/day which will receive wastewater and pump it to SBOS.
The pressure sewer pipeline D800mm from KPK-2 to the sewage treatment plant was built in 1981, financed as part of sewer collector No. 1. The length of one line is 4.5 km (2 lines). Operation in overload mode and the influx of storm water led to complete physical deterioration of the pipeline. Currently, work has been carried out on the installation of a 1020mm pipeline from KPK-2 to the SVHM base; it is necessary to complete construction with the connection of one line of the 1020mm pipeline to the sewage treatment plant.
On the balance sheet of SUE "Vodokanal" there are 49 sewer stations. 16 pumping stations are in need of reconstruction or new construction.
The introduction of foreign-made submersible pumps makes it possible to centralize the control and management of dispersed objects, that is, control from a central control panel, which leads to a reduction in cost; it is planned to bring a number of pumping stations to an automated control system.
The total length of sewerage networks is 166.3 km, with a diameter from 159 mm to 1020 mm, of which at least 50% need to be re-routed due to complete physical wear and tear and low throughput.
In connection with the current situation of water supply and sanitation of the city, there was a need to develop a comprehensive program for the development and modernization of networks and structures of the water supply and sewerage system of Yakutsk, which is aimed at technical restoration and renewal
The water supply of the city of Yakutsk is handled by the State Unitary Enterprise "Vodokanal", which was founded in 1941. The first water supply system facilities were built and put into operation in 1972, and the first sewerage system facilities in 1968.
The scope of activity of the enterprise includes:
Sales of water supply and sewerage services to consumers; - water disposal, wastewater treatment;
Installation and operation of metering units for consumed water and discharged wastewater;
Accounting for water and wastewater consumed by the population and organizations. Facilities maintained by SUE Vodokanal include:
46 sewage pumping stations;
166 km. sewer networks;
108.4 km of water supply networks;
Water intake structure;
Biological wastewater treatment plant
The Lena River is low-lying and has a high sediment content, especially during flood periods. Water treatment is carried out first by coarse filtration through fiber filters installed on the intake pipes. After this, the water is disinfected by chlorination. The quality of water in the Lena River is very variable and the city’s need for water today exceeds the capabilities of high-quality water treatment; therefore, the water intake is being reconstructed and a water treatment plant is being built.
The city of Yakutsk has a drainage system consisting of domestic sewerage and storm sewerage. The State Unitary Enterprise “Vodokanal” is in charge of only the domestic sewerage system; storm sewerage is not the responsibility of the enterprise. The main part of the system consists of two parallel collectors, laid in the central part of the city underground at a depth of 14.5 m. Waste water is supplied to each of the collectors. From the collectors, wastewater is supplied by main pumping stations through pressure pipelines to sewerage treatment plants. Wastewater flow amounted to 17.96 million cubic meters in 2006. 65% of the entire sewerage system is in disrepair and needs urgent reconstruction.
Due to the fact that the Lena River belongs to water bodies of fishing significance of the 1st category and the discharge of treated wastewater is carried out within the city limits, a Biological Wastewater Treatment Station was built, which provides for deep treatment of wastewater with the simultaneous removal of nutrients. SBO acceptance certificate
The property of the enterprise is state property of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). The authorized capital of the enterprise is 35.5 million rubles, the initial cost of fixed assets is 1206.7 million rubles. Depreciation of the enterprise's fixed assets is 515.8 million rubles, which is 57%. The company carries out major repairs and modernization of fixed assets on its own and by contractors. At the expense of the cost of services, repair work was carried out in 2006 in the amount of 38.8 million rubles, at the expense of depreciation charges - 22.7 million rubles.
The main directions of development of the enterprise include the following set of measures:
Reducing unproductive water losses;
Improving the reliability of the water supply system; -increasing the daily volume of water supply;
Reconstruction of existing and construction of new water supply and sewerage networks;
Ensuring a set of international drinking water quality standards;
Improving the quality and environmental safety of wastewater treatment systems.
In accordance with the Investment Program of the State Unitary Enterprise “Vodokanal” for the development of water supply and sanitation systems in Yakutsk for 2008-2012, the list of main activities includes:
1. Development of water supply and sanitation systems in Yakutsk
2.Construction and modernization of main water supply and sanitation facilities
3.Construction and modernization of main networks and water supply and sanitation systems
4.Construction and reconstruction of water supply and sewerage networks
5.Construction and relocation of ownerless water supply networks requiring replacement
The practical implementation of the Program activities will achieve:
1. Eliminate the shortage of drinking water consumption in Yakutsk
2. Provide water supply that complies with GOST
3. Will help avoid environmental disasters and outbreaks of infectious diseases
4.Reduce operating costs of the enterprise
The city of Yakutsk, founded 374 years ago, was built and lives on permafrost soils. In recent years, anthropogenic impact on the upper horizons of the permafrost zone over such a long period has led to significant changes in engineering-permafrost, hydrogeological and geochemical conditions throughout the entire territory.
The problem of flooding and watering of urban areas arose more than 40 years ago, after the start of mass construction and commissioning of stone comfortable buildings. The intensive pace of construction of both residential and industrial buildings has necessitated the occupation of free areas, which remain in the city's territory in oxbow and lake depressions, which represent a system of natural drainage of supra-permafrost and surface waters. Filling low-lying areas and the massive construction of stone buildings, the construction of road embankments, completely blocked the flow of supra-permafrost waters from intra-block areas, reduced the area of moisture evaporation, which together led to the development of flooding and watering processes. Flooding and watering of the territory of Yakutsk negatively affect the stability of the foundations of buildings and structures, road surfaces, underground pipelines and other engineering facilities.
The main difficulties that significantly complicate the effective fight against flooding and watering of the territory of Yakutsk:
1. The built-up area of the territory, which, together with the existing underground systems for laying cable, water-carrying, gas and other communications, significantly complicates the use of optimal drainage schemes for surface and supra-permafrost waters.
2. The impossibility of using standard drainage designs and storm sewer systems due to the harsh climatic and complex permafrost-hydrogeological conditions of the area, as well as insignificant slopes of the day surface.
3. High regulation of above-ground flow by road embankments, buildings built according to the first principle, additions of imported soil during planning work on construction sites, which significantly complicates the normal functioning of drainage systems and storm sewer systems.
4. The impossibility of discharging drainage water and storm water into the city sewer due to overload due to the increasing volumes of domestic wastewater. In addition, the high mineralization, aggressiveness, toxicity and bacterial contamination of above-ground waters does not allow their discharge into surface urban watercourses and reservoirs without preliminary treatment.
The listed difficulties indicate the extreme complexity of combating flooding and watering of urban areas. In the spring, when flooding occurs, roads are destroyed, the strength of the soil foundations of buildings and structures is reduced, which leads to their deformation. To eliminate such situations, a large amount of unnecessary human and material resources are spent annually.
Program activities until 2012 are a continuation of the activities of the Municipal Target Program “Providing water drainage from the territory of the city of Yakutsk for the period from 2005-2008” and provide for two main blocks of activities in the amount of 1,200 million rubles, including:
11. Reconstruction of the Big and Small Rings of the City Canal - 500 million rubles.
12. Construction of storm sewerage with treatment facilities - 700 million rubles.
As a result of the implementation of program activities, it is planned to achieve
Reducing unplanned costs for pumping melt and storm water;
Increasing the service life of road surfaces;
Increasing the reliability, quality and timely drainage of melt and storm water.