Low-voltage networks - project. What are low-voltage systems Design of internal low-voltage systems
Low-voltage cables are cables and wires through which a weak current flows with a voltage of not more than 25 V. They are used in enterprises, residential buildings and offices. It is difficult to find a modern room in which a low-voltage network would not be laid.
Application
It must be said right away that a weak current is meant, measured in milliamps (mA).
Weak alternating current can carry an information signal, which is used in the following areas:
- Television.
- Radio communications.
- telephony.
- Computer networks.
- Alarm systems.
Low-current cables for telephone lines and antennas were the first to appear. Twisted pair was invented by Bell at the end of the 19th century. Over the past 20-30 years, engineers have developed a huge number of types of low-voltage cable products. It is intended for use in everyday life and in highly specialized areas. Internet, satellite TV, wired telephone and computer networks are indispensable without low-current cables.
twisted pair device
To transmit communication signals, insulated and twisted pairs of wires are used. To ensure the unity and strength of the structure, twisted pairs are placed in a plastic shell. Use one, two or more pairs, depending on network requirements.
Twisting is necessary to reduce the electromagnetic influence of the wires on each other, reduce capacitive losses and create an obstacle to external interference.
Cables with twisted pairs of wires are used to organize networks for video surveillance, telecommunications, security systems and computer networks. The twisted-pair wire system is popular due to its low cost and easy installation.
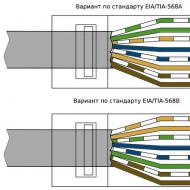
You can connect the cable to devices using the unified 8P8C connector, which has 8 pins and a lock (RJ-45 connector).

To protect twisted wires from chemical, mechanical and electromagnetic effects of external factors, a polyethylene sheath, metal braid and foil are used.
A pair is made of single-core and multi-core wires. Stranded wires perfectly tolerate twisting, bending, so they are used in patch cables and cords that connect electrical devices and equipment. Single-core twisted pairs are laid in ducts and walls where there are no strong bends.
Since in English "twisted pair" sounds like a twisted pair, the abbreviation TP is used to designate it. To understand a shielded cable or not, you need to pay attention to the markings. According to international standards, the following designations are accepted:

- U - no shielding;
- S - a metal braid is used;
- F - aluminum foil is used.
Thus, the designation U / FTP indicates that foil shielding is provided to protect each pair, there is no common shield. SF / UTP - there is a common shield of foil and braid, there is no separate shielding.
Depending on the frequency range passed by the TP cable, it is classified into one of 8 categories. The higher the category, the more steam is contained in the cable and the greater the density of turns per pair. The first category was used on old modem lines and in telephone communications, the eighth category is used for the construction of computer networks with a data transfer rate of 40 Gb / s.
Coaxial cables
Coaxial cables are used to transmit radio waves. They consist of a conductive core and a coaxial screen. Between the core and the screen is a layer of insulation.

On top of the screen is a protective shell, which is made of fluoroplastic, PVC or polyethylene. The shell must protect against moisture, mechanical damage and be resistant to ultraviolet radiation. In addition to this, it serves as a breakdown protection.
The screen performs the function of grounding and is an external conductor, so it is made from a braid of wires, foil or other structure with conductive properties. The braid can be combined with foil, in which case the screening will be double.
In conditions of strong interference, cables with a double layer of foil and a double layer of braid are used.
The center conductor is most often made of copper wire or several copper wires twisted into a spiral. Alloys of copper, aluminum and steel are used.
In relation to isolation, there are also requirements. It must fit snugly against the conductors and ensure perfect alignment.
The requirement for exact coincidence of the axes of the central conductor and the screen is not accidental. With such a mutual arrangement, the electromagnetic field is completely concentrated inside the wire in the insulation layer, and the energy loss for radiation tends to zero. In addition, the cable is protected from external interference, which allows you to keep the purity of the signal.
Coaxial cables are used wherever high frequency electromagnetic signal transmission is required. There are also models that are used to transmit a low-frequency signal.
Depending on the diameter of the section, 2 types of coaxial cables are distinguished:
- Thin flexible (thin) with a diameter of about 6 mm with a wave impedance of 50 ohms, often used to build computer local area networks.
- Thick hard (thick) with a diameter of about 12 mm for data transmission over a distance of up to 500 m at high speed.
According to the Radio Guide (RG) scale, cables are divided into several categories. In satellite and cable television, the categories RG-59 and RG-6 are used, for military purposes RG-58C / U, for the main laying of RG-11. Thin cables are RG-58, and thick cables are RG-11 and RG-8.
Television cables of the SAT-50 and SAT-703 categories are widely used.
The SAT designation is the marking of the Italian company CAVEL. Other manufacturers may use their own type marking (PK-75 with 75 ohm impedance) .

Auxiliary elements are provided for connecting coaxial cables to each other and connecting them to various devices. These are connectors, adapters, tees, which are produced either together with the cable, or separately.
Low-voltage cables and wires for telephone networks
Although many people think that wired telephone communications are irretrievably a thing of the past, telephone cables are still in demand. In many areas, they are considered an inexpensive and most affordable way to ensure the transmission of an electrical signal.

The following markings are provided for them:
- T - telephone;
- L - linear;
- P - polyethylene sheath;
- B - PVC sheath;
- Z - there is a placeholder;
- B - there is armor;
- Sh - hose (sometimes made of Shp polyethylene or Shv polyvinyl chloride);
- ep - film screen;
 (Green, Red) - Analog Phone (Yellow, Black) - Special Phones
(Green, Red) - Analog Phone (Yellow, Black) - Special Phones For laying telephone networks, low-current cables and wires are used, designed to connect a large number of subscribers or intended for single wiring (in a separate apartment, private house, etc.)

TRV, TRP are morally obsolete, but low-current cables continue to be used in some areas, colloquially called “noodles”, because the wires in them run in parallel without twisting. They are used for fire alarms and for connecting indoor telephones. TRP cable has a more reliable polyethylene insulation, so it can be laid outside buildings.

CCI brand cable products are widely used. They are laid in mines, tunnels, trenches, collectors, and other underground structures, and are used to build urban telephone networks. The number of pairs in the CCI cable can be from 5 to 600.
Fiber optic cables
To transmit an optical signal, fiber optic cables are used, the fibers in which are made of plastic or glass.

The main parts of the cable:
- Fibers (8-144 pieces), covered with a layer of transparent or colored varnish.
- Plastic tubes containing 4-12 fibers and a water-repellent gel.
- Braiding film.
- Carrying rope.
For additional protection, a hydrophobic film and a Kevlar coating are used.
Because fiber optic cables are relatively new, there are no standards for fiber color coding. Each manufacturer produces products with fibers of the color they see fit. Deciphering their meaning is given in the instructions.
The advantage of using a fiber optic product is high signal transmission speed, low attenuation over long distances, and a high degree of information security from hacking. As a result, information is transmitted quickly and efficiently. Low current cables of this type are a new generation of cables, the production technology of which continues to improve.
The installation of low-voltage systems is a complex process, the correctness of which largely determines the functioning of the company and the speed of the information flow. The importance of these systems is so high that there can be no question of any savings. It is necessary to use only modern equipment, the best technologies and involve experienced and professional workers in the installation process.
Low-current works include the installation of video surveillance systems, office telephony, local networks, security and fire alarms, as well as access control systems.
Local networks. The work of any company and no office can be carried out without the organization of a local network. It includes peripheral equipment, telephones and computer equipment. The first stage of the installation work of this system most often begins before the requirements of network users regarding the type of network flow and the speed at which data must be transmitted become known. Installation of a local network creates the basis of a computer network, which is later combined with a telephone network. Both of these networks, when integrated, create a local network.
CCTV. Thanks to low-current work on the installation of video surveillance systems, it becomes possible to control and visually monitor all areas of a building or office. In addition, the installed video cameras allow you to record video online, which increases security several times and protects the company's property from possible theft.
Office telephony. Reliable high-quality telephone communication in the office and beyond is ensured by means of office telephony - mini-PBX, departmental PBX and PBX for the office. Installation of office telephony increases the efficiency of its use and reduces the cost of its maintenance. It is due to ease of use, high quality communication and affordable prices that PBX is so popular. Now you are not in danger of hearing noise in the handset or fighting constant interference. The main thing is that the installation of office telephony should be carried out by professionals, taking into account all the rules and regulations.
Access control systems. Installation of access control systems allows you to effectively determine the time spent by personnel in the company's office and control the work of employees, as well as introduce restrictions on access to individual office premises.
Thanks to the installation of access control systems, it is possible to organize a database for each client and visitor, control access to office premises, keep a competent record of employees' working time and solve other important tasks.
Security and fire alarms prevent unwanted persons from entering the territory of the office, as well as notify emergency services in the event of a flood or fire.
Low-voltage networks are an integral element of the design of absolutely any modern building. Each next year, along with the improvement of technology, brings us a significant increase in the volume and complexity of the applied networks.
Today, low-voltage networks include:
- Local Area Networks (LAN);
- Structured Cabling Systems (SCS);
- Warning systems;
- Telephony systems;
- clock;
- Radiofication;
- Broadcast and cable television;
- Security alarm;
- Fire alarm;
- CCTV.
The design of low-voltage networks is an important step in the construction of absolutely any type of building. It is their use that will largely determine the levels of life support, comfort and safety when working or living inside. Agree, it is difficult to imagine a modern house not equipped with security and communication systems.
Before designing, a pre-project survey of the selected development object is carried out. This stage is obligatory in order to define a set of measures and develop technical proposals. The result of the survey by certified specialists is the preparation of optimal technical solutions to optimally meet any customer need, with which the design specification will be drawn up in the future. The terms of reference is one of the basic data for designing low-current systems. It is in the terms of reference that all requirements for low-current systems (composition, cost, placement, interaction with other objects) should be defined.
The basis for drawing up the terms of reference is the technical requirements imposed by the customer. That is why the task is developed jointly with the customer - in this way, the wishes and goals of the latter are clarified when creating a complex of low-voltage networks at the facility and their further implementation. Competent setting of goals in the terms of reference is a guarantee of fast and high-quality implementation of the object. Specifications, which are also used to form the task, can be issued by communication service providers (telephony, radio, television) and operating organizations (when the tenant's network is connected to an existing one in the building). Another initial component of the terms of reference is related sections in engineering systems: design project, master plans of engineering networks and architectural solutions, ventilation project, power supply, etc.
After agreeing the TOR with the customer and receiving the initial data, the process of designing low-current systems begins. The room is determined in which (depending on the type of low-voltage network) the control room, server room, fire station, etc. will be located. Each of these premises has its own requirements for area, fire resistance and fire safety. Next, places for the passage of electrical and low-voltage risers, trunk communications, as well as methods for laying cables in rooms and the type of installation for terminal elements will be determined.

The design may consist of one stage ("WP" - working draft), or two stages ("P" - project and "RD" - working documentation). When using two-stage design, the project must first be completed, which is then sent for examination. The “P” should indicate the fundamental decisions on the general organization of a low-voltage network, which, when passing the examination, will be considered, evaluated and, if necessary, corrected. The agreed stage "P" will become the basis for further development of working documentation. The "RD" will detail the solutions that are installed in the project. Based on it, an estimate will be drawn up and construction and installation work will be performed.
The result of the completed design is a project designed in accordance with all standards. It must include the following components:
- Title page;
- Cover;
- The composition of the project;
- Explanatory note;
- General information about the project;
- Block diagram of the designed network;
- Plans for the layout of cable routes and the location of equipment;
- Sketches according to which the equipment is placed;
- Cable magazine;
- Equipment specification.
The specialists of our company will design low-voltage networks of any complexity for you. From an apartment to a modern multi-storey office building or a shopping center
The Internet, television, telephone, security systems, access control, video surveillance - all this can be combined under one term "low-voltage networks". Low current networks(SS) and systems define the security structure of the building, the information support structure of the object, whether it is a residential building or a shopping center, or a factory floor, a drilling platform or a pipeline system. Listing the SS systems, they can be divided into several groups: communication networks (Internet, television, radio, warning), access control systems (video surveillance, burglar alarms, access control systems), fire safety systems (AUPS, SOUE), dispatching and engineering systems management systems and mechanisms, automated process control systems (APCS), systems of anti-terrorist protection and security of the capital construction object.
Design of low current systems
Given the increasing prevalence of various low current systems, the design of SS is a necessary process today. In accordance with the rules and regulations, the "low-voltage networks" section is an integral part of the project documentation for construction projects.
According to the terms of reference of the Customer, the specialists of our organization professionally develop the section Communication networks And low current systems. The execution of documentation can be carried out both for a complex of low-voltage systems, and for individual components (for example, security systems).
We design various types of low current systems
Telephonization- acts as a system of modern telecommunications, with ample opportunities for voice transmission of information, both within objects and retransmission to external sources. IP-telephony is widely used today. IP-telephony allows the use of any IP-network (Internet, local area networks, dedicated channels) as a means of telephone communication, with all its inherent useful properties, such as long-distance and international telephone calls or fax transmission in real time.The design of telephony includes the wiring of networks inside the building, the installation of equipment - automatic telephone exchanges, as well as external telephone networks (overhead lines or a cable laid in the sewer).
Automatic telephone exchanges are classified as analog, digital and hybrid. For a small number of subscribers mini-ATS are used. As a rule, in modern construction, digital systems are used that allow the use of an almost unlimited number of signals, while analog phones, IP, and software can act as subscribers.
Internet- it's hard to imagine that ten years ago the Internet for most of us was something special, bewitching, attractive... Fi signal to our laptops. Laying the cable, setting up access points, determining the characteristics of the network - all these are the tasks of the designer of WWW networks.
SCS- our company offers design structured cabling system(SCS). The implementation of projects is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the international standard ISO / IEC 11801. We design and select equipment in accordance with the standards and preferences of the customer. The development of a working project allows you to perform reliable and durable SCS systems. When designing the SCS system, a reserve is considered and laid down for the further development of the facility, as a result of which, when organizing new jobs or when redevelopment, there is no need to lay additional cable lines.
Local area network (LAN)- this system is connected by one or more autonomous high-speed digital data transmission channels (including wired, fiber optic, microwave radio or infrared) within one or more nearby buildings.
Radiofication- transmission of sound over a distance by means of radio waves. The system itself is an organization inside the building of an antenna tuned to certain radio frequencies. And although the use of a radio point in residential buildings has already gradually become an atavism, nevertheless, there are objects for which the design of radio is a mandatory phenomenon, and the systems are tuned to the signals of the Ministry of Emergency Situations and other services (typical for industrial facilities).
Cable TV- a cable television system is designed to receive, process and transmit television signals via a fiber-optic or high-frequency cable for the purpose of their subsequent distribution to the consumer.
Video surveillance system- provides transmission of visual information about the state of protected zones, premises, perimeter and territory of the facility to the security premises.
This system allows not only control and recording of external and internal surveillance, but can also be integrated with access control and burglar alarm systems into a single integrated security system.
Access control and management system(ACS) - is designed to provide authorized entry into the building and into restricted areas and exit from them by identifying a person by a combination of various features: a real code (Wigand cards, touch-memory keys and other devices), a memorized code (keyboards, code dialers panels and other devices), biometric signs (fingerprints, retina and other signs), as well as preventing unauthorized access to the premises and restricted areas of the facility.
Ensuring access control to the facility (for industrial buildings) has recently been carried out by a design engineer (Government Decree No. 87, section Technological solutions).
our company designs ACS for industrial facilities, office buildings, special purpose facilities. ACS allows you to solve both security issues and control of the working time of personnel without involving a large number of duty and security workers, in some cases it allows you to fully automate the process of access to the facility. The access control and management system can be combined into a single building engineering systems management network or a “smart home” system.
Security Alarm System (SOTS)- is a set of jointly operating technical means for detecting intrusion (attempt of intrusion) on a protected object or area of premises, collecting, processing, transmitting and presenting information about intrusion (attempt of intrusion) and other service information in a given form.
All premises with permanent or temporary storage of material assets, as well as all vulnerable places of the building (windows, doors, hatches, ventilation shafts, ducts, etc.), through which unauthorized entry into the premises of the facility is possible, should be equipped with security alarms.
Fire alarm system AUPS - designed for prompt detection of fires at the initial stage of their formation, as well as for generating signals that control fire warning systems, launching various engineering equipment and automatic smoke removal and fire extinguishing installations.
Fire alarm system SOUE. The warning system is created to promptly inform people about an emergency situation that has arisen or is approaching (accident, fire, natural disaster, attack, terrorist act) and coordinate their actions. The system also includes functions for managing the evacuation of people.
Security and protection deratization system (OZDS), designed to expel rodents from the territory of the property and prevent their entry from the outside by exposing them to a high voltage electric current. Additional factors of the operating OZDS are sound and electromagnetic radiation, as well as the presence of traces of ozone, which are perceived by rodents as signs of an upcoming repeated electric shock and contribute to their refusal to inhabit the equipped facility.
ASKUE- designed for automated quality control and accounting of consumed electricity. The ASKUE system collects primary data on energy consumption indicators for each customer facility, calculates, stores and analyzes the calculated indicators, and also provides the preparation and issuance of the necessary information for administrative management or to the control panel of the EnergoSbyt enterprise. The system automatically transfers data to the Energosbyt control panel via a telephone line or a GSM channel, eliminating the need to take readings manually. With the help of this system, the performance of metering devices is monitored and data on electricity consumption is promptly processed.
Request a quote and prices
Submit an inquiry
The engineering arrangement of modern buildings, regardless of the purpose, provides for the presence of low-voltage wiring. Such networks, unlike power electric cables, are focused on providing communication links. Their tasks may be different, but the main unifying characteristic is to support voltage from 12 to 24 V. That is, low-current networks can run parallel to power supply circuits, but are in no way associated with their function. About what tasks such a network performs, how it is organized and mounted, it is worth talking separately.
Purpose of low-voltage infrastructure
There are no restrictions on the use of such networks - they are used in the communication support of residential buildings (private and multi-apartment), buildings of commercial enterprises, at industrial facilities, in vehicles, and even as part of engineering structures. Depending on the characteristics of low-current systems, they can participate in solving the following tasks:
- Receiving a cable TV signal.
- Internet access.
- Telephone access.
- Ensuring the operation of wired radio.
- Energy resource management.
- Control of electrical equipment.
- Support for the functions of local area networks.
- Ensuring the operation of security and fire alarm systems.
As you can see, the list of tasks is extensive and some of them can be found today in any modern house, while others are successfully solved in production, in the construction industry, etc.
Network device
The basis of any electrical network is formed by cable lines. Low-current wiring uses a wide range of cables, which will be discussed below. But for now, it is important to emphasize that a full-fledged working infrastructure of such a network is not complete without telecommunications equipment and cable boxes. These are systems thanks to which the laid circuits transmit a signal with the necessary parameters. The list of telecommunications equipment includes connecting elements, patch panels, cable connectors, modular jacks, sockets, etc. That is, we are talking about electrical fittings that support network functions. Also, the device of low-voltage networks provides for the inclusion of cable boxes. There are three types of this equipment - equipment racks, distribution cabinets and cable boxes directly. Instrument racks provide the physical placement of equipment. These are in some way bearing and supporting devices for ergonomic placement of equipment.
Distribution cabinets serve wiring, providing it with sockets, plugs and other connectors, connecting to which one or another cable gains access to a signal source or consumer. As for cable boxes, they are used for the safe maintenance of lines in places of nodal transitions from one laying zone to another.

Traditional low current wiring
Most of the existing low-current lines are formed by classic twisted pair and coaxial wiring. Cables of the first type are wires twisted in pairs and provided with insulation. Twisting one or more pairs is required to minimize electromagnetic interference from outside, reduce capacitive losses and eliminate interference. In order to protect against mechanical and chemical influences, a durable outer sheath is also used. Depending on the threats, polyethylene, metal or foil braided cables can be used. Typically, twisted pair is used in the organization of video surveillance systems, network computer and telecommunications infrastructure. With the help of twisted pair, low-voltage networks are inexpensive and easy to install, but their immediate performance in the form of data transfer volumes and signal quality still forces consumers to switch to more modern options. One of the alternative solutions at one time was a coaxial cable. It is more often used to transmit radio waves and in other tasks where the transmission of an electromagnetic signal is required - high or low frequency. The cable itself of this type is formed by a conductive core (copper, steel or aluminum wire), an insulation layer and a shielding protective sheath.

telephone wiring
It is also a kind of cables that are gradually becoming a thing of the past, but are still used at facilities where high costs for more productive, but expensive wires are impractical. The telephone cable is focused both on the possibility of performing a single wiring, and on connecting a large array of subscribers. The "long-livers" of this segment include the types of cables TRV, TRP. They are mainly used in the organization of telephone lines indoors, as well as in fire safety systems. Although some modifications of the TRP due to polyethylene insulation can be laid outside buildings. The most technologically advanced low-current electrical telephone networks are based on CCI cables. Such products can be used in tunnels, collectors, mines and other channels of outdoor and underground laying.
Modern fiber optic wiring
Such cables are fundamentally different from the analogues described above both in terms of the principle of operation and the device. As for the first, the cable works with an optical signal, transmitting it through fiberglass fibers. Accordingly, the device of the wire is also determined by this transmission method. The main elements of a fiber optic line include the following:
- Fibers in the amount of 8 to 144 pcs.
- Plastic pipes, which accommodate from 4 to 12 fibers.
- Braid.
- Hard rope.
Depending on the application, such a cable can be provided with a standard plastic protective sheath, hydrophobic film, or high-strength Kevlar insulation. In terms of performance, low-current systems based on fiber optic wiring have many advantages, including high signal transmission speed, effective protection against third-party information and reduced attenuation when using lines over long distances.

Operational requirements for networks
One of the main requirements is a high degree of reliability. The laid lines must meet modern standards for technical and information security. Next, the operability of the network is taken into account, regardless of external influences. The system should have minimal risks of failures and errors. This part also takes into account the human factor and energy loads on the line. To ensure this kind of protection, automatic control and management tools are increasingly being introduced. At the same time, low-voltage networks are organized with the possibility of further expansion, modernization and reorientation in terms of their intended purpose. A modern communication system must be flexible and scalable. In addition, requirements such as energy efficiency, economy and accessibility for installation are not excluded.
Network design

This is the initial stage of work in the organization of low-voltage infrastructure of the facility. The project can be carried out both at the construction stage of the building and during its operation. In both cases, the characteristics of the object are initially analyzed, possible risks, options for interaction with adjacent systems and laying methods are assessed. At this stage, the communication service provider and the consumer directly are also connected, who make their requirements and recommendations. At the end, the designers submit a technical document that describes the practical networking plan. In particular, a description and a visual schematic representation of the future low-voltage network is provided, indicating wiring lines, equipment placement points and technological rooms. For example, a structural plan may contain a visual model with the locations of low-voltage risers, main communications, and terminal elements. The most complex projects include separate sections with descriptions of server rooms, fire stations to ensure the safety of lines, control rooms and other functionally significant points.
Methods for laying low-voltage networks
According to the laying methods, communication networks differ slightly from power networks. The safest is the underground laying channel. The so-called cable duct, for which trenches are specially dug. But in the implementation of this method of placing lines, only special cables with an armored sheath can be used. The overhead version of the laying is also common, which has its advantages. By hanging on the supporting structures, outdoor low-voltage air-type networks are organized, available for maintenance and renovation. Where possible, wiring may be moved from building to building or incorporated into existing power lines.

Installation work
The approach to installation work is determined by the type of network, its purpose and characteristics. First of all, the installation of communication equipment is carried out - distribution cabinets are fixed and filled with functional devices, the target signal receiving equipment is placed, etc. Then work is done to prepare the channels for laying. As already mentioned, these can be trenches, support structures for overhead lines, as well as special trays for integrating cables. Up to the terminal device, the installation of low-current networks is usually implemented using solid wires without splicing. The same telephone cable can run in the same direction with the same circuit, but in parallel. A prerequisite for installation work is the inclusion of protective systems in the infrastructure. For example, when organizing air networks, an electrical protective device with grounding should be provided at the cable entry points into the building.
Requirements for installation work
To ensure the efficient operation of the network, special rules have been developed that the project implementer must adhere to. The main ones look like this:
- If the cables are laid in parallel with the power wiring, then a minimum distance of 50 cm between the circuits must be maintained.
- It is forbidden to run cables into distribution nodes that already contain elements of other types of networks.
- Electrical boxes to which a low-current cable network is connected should be placed on the walls, but at a distance from window and door openings.
- For critical communication lines (in medical institutions or at fire safety stations), it is recommended to arrange wiring in raised floors and channels made by gating.
Finally

In Russia, regulatory documentation for the design and installation of communication networks is still only partially presented. Many aspects of the organization of this infrastructure are not affected at all, so specialists have to turn to foreign regulations and standards. However, since low-current and power networks converge in certain operational parameters, old domestic recommendations for laying electrical networks are often used. In addition, manufacturers of telecommunications equipment provide a lot of information to perform the correct installation. At the same time, financial problems persist that do not allow enterprises to switch to new standards of low-current signal transmission.